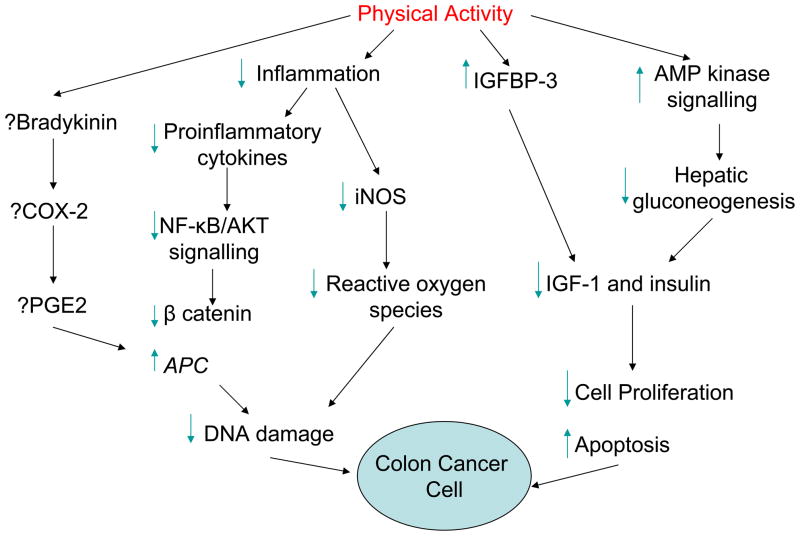
Fig. 1.
Hypothesized mechanisms of physical activity in colon cancer. Physical activity may block inflammatory pathways, resulting in downregulating nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB)/AKT signaling, decreased development of oxidative species, and less DNA damage. Physical activity may also affect the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) pathway and AMP kinase signaling, resulting in lower levels of cell proliferation and increased apoptosis. The effect of physical activity on cycloxygenase-2 (COX-2) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) levels is unclear (47–50, 54). IGFBP, IGF binding protein; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; APC, adenomatous polyposis coli.