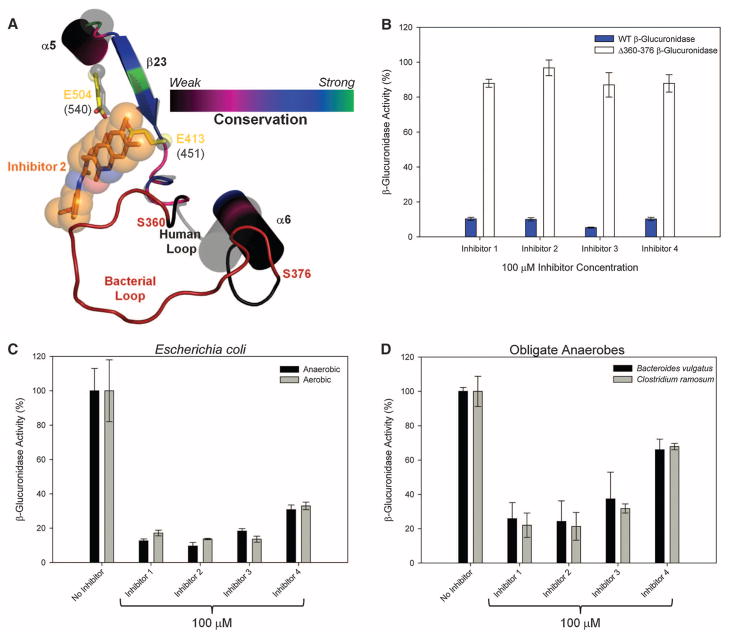
Fig. 3.
Inhibitor selectivity for bacterial β-glucuronidase. (A) The 360–376 loop forms direct contact with the bound inhibitors in the E. coli β-glucuronidase structure. This loop is missing from the structure of human β-glucuronidase; thus, it is labeled the “bacterial loop.” (B) Elimination of the “bacterial loop” from E. coli β-glucuronidase produces an enzyme insensitive to inhibitor efficacy. (C) β-Glucuronidase inhibition in living E. coli cells grown under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. (D) β-Glucuronidase inhibition in two obligate anaerobic bacteria. Error bars represent SD; N = 3.