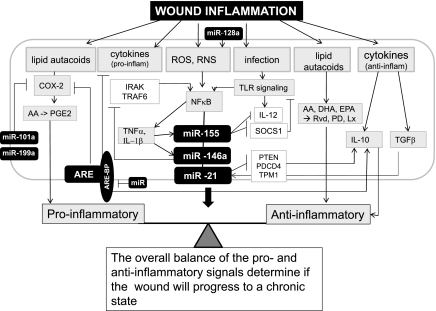
Fig. 1.
Potential role of microRNA (miRNA, also miR) in regulation of wound inflammatory response. The inflammation response to wound is tightly regulated by proinflammatory signals as well as signals that are anti-inflammatory to resolve inflammation. An imbalance between these signals results in chronic inflammation and derails the healing cascade. miRNA have been shown responsive to as well as regulate some of the key mediators of inflammatory response in the course of wound healing. The details of the miRNA or mediators have been discussed in the review. miRNA regulate the expression of the components of the ARE-BPs that are known to regulate cytokine and Cox-2 gene expression. The miRNA and the targets of miR have been presented as filled and open boxes, respectively. AA, arachidonic acid; ARE-BP, AU-rich element binding protein; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; DHA, docosahexaenoic acid, EPA, eicosapentaenoic; Lx, lipoxin; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; Pd, protectin; RvD, resolvin; ROS, reactive oxygen species; RNS, reactive nitrogen species; TLR, Toll-like receptor.