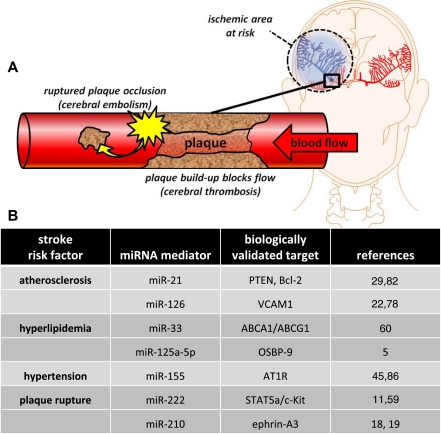
Fig. 1.
Ischemic stroke etiology. A: a thrombotic stroke occurs when diseased or damaged cerebral arteries become blocked by the formation of atherosclerotic plaque within the brain. Clinically referred to as focal cerebral thrombosis or cerebral infarction, this classification of stroke is responsible for half of all clinically presented stroke cases. An embolic stroke is also caused by cerebrovascular occlusion of atherosclerotic plaque origin, but in this case the plaque (or emboli) ruptures from a distal site, travels in the blood, and occludes a distal point in the cerebrovascular system. B: biologically validated miRNA identified to play a role in ischemic stroke etiology.