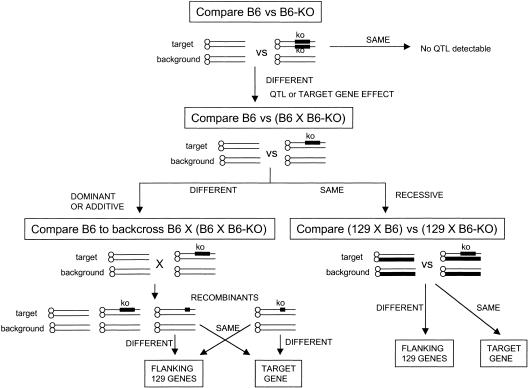
Figure 1.
Strategy for determining whether a specific phenotype is the result of the ablated target gene or the flanking 129 genes. Comparisons are made to determine the cause of the genetic effect (target or flanking) as well as its mode of inheritance — dominant, additive or recessive. Lines represent chromosomes; target indicates the chromosome with the mapped target locus; background indicates the other 19 chromosomes. KO indicates that the chromosome contains the targeted ablation. Heavy lines indicate that the origin of the chromosomal segment is 129. Thin lines indicate B6 chromosomal segment origin. B6-KO indicates that a strain is homozygous for the targeted ablated or knocked out region. In a B6 congenic/knockout strain, after N9, >99.8% of the unlinked genes are of B6 origin. Arrows indicate the next step to be taken in scheme.