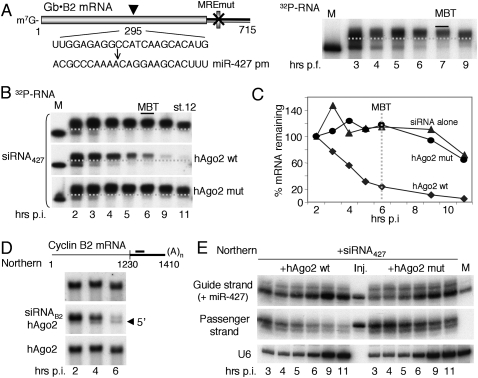
Figure 5.
Lack of endogenous xlAgo2 catalytic activity in early embryos. (A) Inactivity of a coding region miR-427 target site. A 32P-labeled Gb•B2 reporter RNA with a perfect match miR-427 target sequence within the β-globin coding region and an inactive MREmut in the 3′ UTR was injected into one- to two-cell embryos and analyzed as in Figure 1A. Note that the miR-427pm target site in the coding region does not elicit deadenylation at MBT. (B) siRNA427-guided RNAi in preMBT embryos. The 32P-labeled reporter RNA plus siRNA427 (20 fmol per embryo) was injected alone or together with synthetic mRNAs encoding wild-type or mutant Myc-tagged hAgo2 and analyzed as in A. (C) Both 5′-terminal and 3′-terminal cleavage products were detected in the presence of hAgo2wt (Supplemental Fig. S3), and the extent of RNAi was quantified by PhosphorImager analyses. (D) siRNAB2-guided RNAi of endogenous cyclin B2 mRNA. Synthetic mRNA encoding wild-type myc-tagged hAgo2 was injected alone or together with siRNAB2 (30 fmol), and mRNA stability was monitored by Northern blot analysis of full-length cyclin B2 mRNA. The arrowhead indicates the 5′− terminal RNAi cleavage product. siRNAB2 targets the 3′ UTR of X. laevis cyclin B2 mRNA (black bar in top schematic). (E) Ago2-mediated destabilization of the passenger strand of siRNA427. Samples shown in B were analyzed by Northern blot hybridization using probes specific for the guide or passenger strand of siRNA427. Marker lanes with one embryo equivalent of total RNA from noninjected stage 9.5 embryos (M) and siRNA427 prior to injection (Inj.) show that the amount of siRNA427 injected was comparable with that of endogenous miR-m27. The increase in guide strand hybridization signals at 5–6 h post-injection reflects the onset of endogenous miR-427 synthesis.