FIG. 1. In vivo activity of A-PGS variants (A) and purification of recombinant A-PGS variants (B).
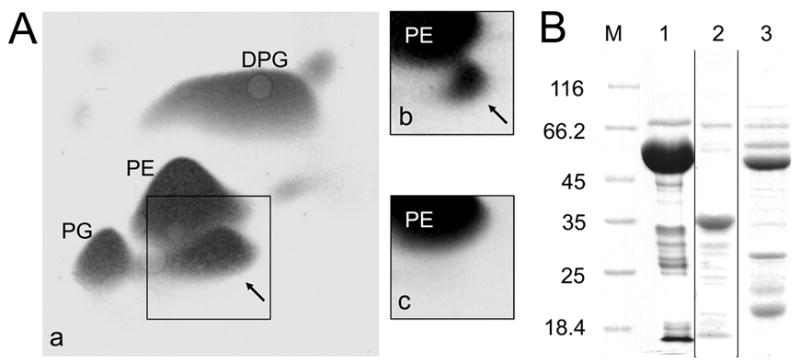
A. Separation of polar membrane lipids by 2D-TLC and detection by 5 % (w/v) molybdatophosphoric acid staining is shown. Lipids were extracted from E. coli cells overproducing GST-A-PGS543-881 (panel a), His6-A-PGS (panel b) and solely GST (panel c) as a negative control. The lipids phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidylglycerol (PG), and diphosphatidylglycerol (DPG) are indicated. Alanyl-phosphatidylglycerol (A-PG) is highlighted by black arrows.
B. SDS-PAGE analysis of purified GST-A-PGS543-881, A-PGS543-881 and GST-A-PGS543-855N proteins. Indicated proteins were produced recombinantly in E. coli BL21 (λDE3), purified chromatographically and subsequently analyzed by 12 % SDS-PAGE and Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining. Lane M, molecular mass marker; relative molecular masses (* 1000) are indicated. Lane 1, purified GST-A-PGS543-881; lane 2, A-PGS543-881; lane 3, purified GST-A-PGS543-855N.
