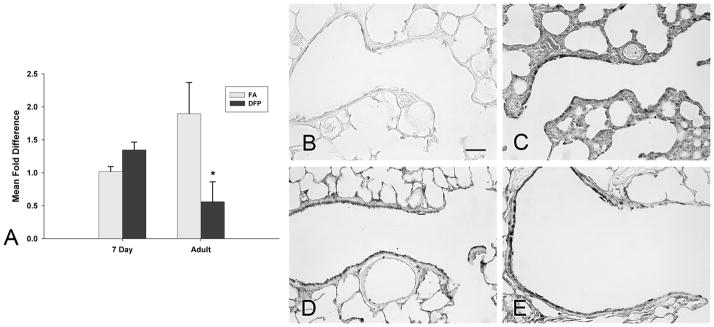
Figure 7.
Gene expression (A) and immunohistochemical staining (B–E) of glutathione peroxidase 1 in the airways of filtered air (B and D) or DFP exposed (C and E) neonatal (B and C) or adult rats (D and E). Gene expression of glutathione peroxidase 1 (A) in microdissected airways was calculated using the comparative Ct method and displayed as a mean fold difference ± SEM (n=3–5 rats/group) compared against FA 7 day postnatal animals using HPRT as the reference gene. After DFP exposure, glutathione peroxidase 1 gene expression remained unchanged in neonates, while a significant decrease in gene expression was found in adults. * = P <0.05, as compared to filtered air controls of the same age. Protein expression in FA 7 day neonates was faint (B) but increased markedly with DFP exposure (C). Compared to FA neonates, protein expression in adult FA exposed rats (D) was higher. After DFP exposure (E), intense glutathione peroxidase 1 positive staining was observed in the airway epithelium but was diminished in the most distal portion of the terminal bronchiole. Scale bars are 50μm.