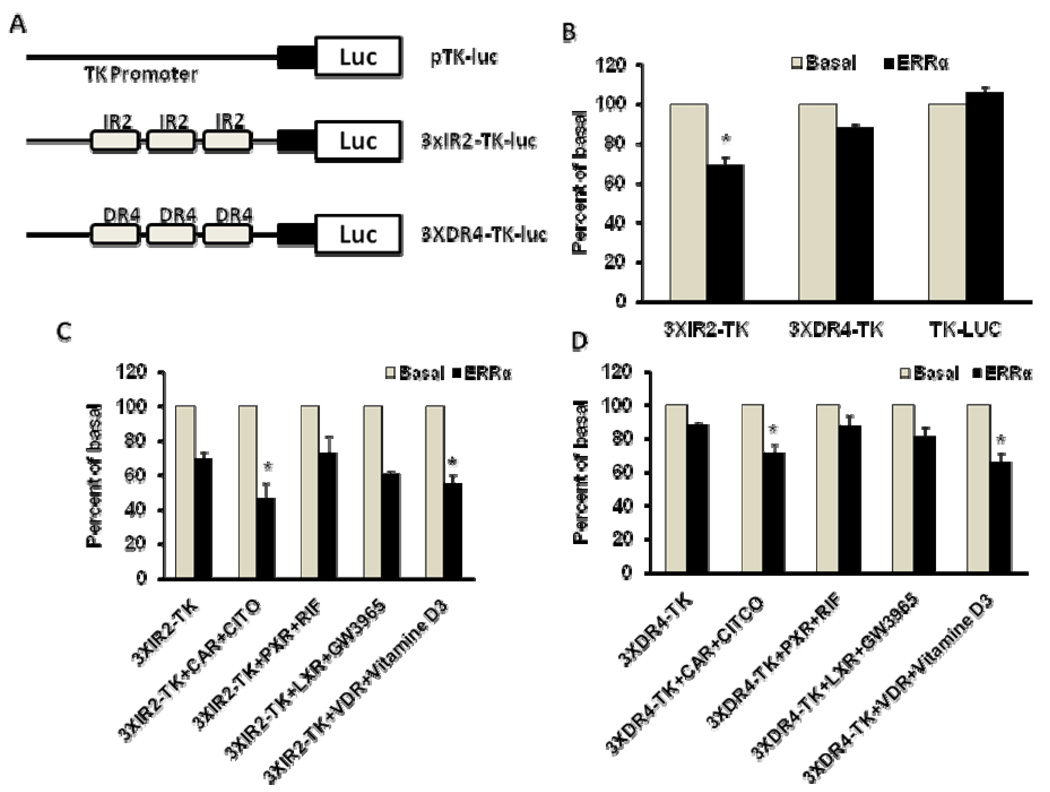
Figure 5. ERRα modulation of SULT2A1 promoter transcription mediated by IR2 and DR4 elements in Hep G2 cells.
A. Schematic representations of pTK-luc, 3XIR2-TK-luc, and 3XDR4-TK-luc reporter plasmids. B. ERRα modulation of IR2 and DR4 reporter transcription in Hep G2 cells. Cells were co-transfected with pTK-luc, 3XIR2-TK-luc, or 3XDR4-TK-luc reporter plasmids (1 µg/well) and with either pCDNA3.0-ERRα expression plasmid (0.25 µg/well) or pCDNA3.0(0.25 µg/well). Data were normalized according to Renilla activity. C. ERRα modulation of nuclear receptor-mediated IR2 reporter transcription in Hep G2 cells. Hep G2 cells were co-transfected with 3XIR2-TK-luc reporter plasmids (1 µg/well) and pCDNA3.0-ERRα expression plasmid (0.25 µg) and nuclear receptor (0.25 µg; CAR, PXR, VDR or LXRα). D. ERRα modulation of nuclear receptor-mediated DR4 reporter transcription in Hep G2 cells. Hep G2 cells were co-transfected with 3XDR4-TK-luc reporter plasmids (1 µg/well) and pCDNA3.0-ERRα expression plasmid (0.25 µg) and nuclear receptor (0.25 µg; CAR, PXR, VDR, or LXRα). Data were normalized according to Renilla activity. The percentage of inhibition was calculated relative to the basal promoter control. Results are presented as means ± SD from three independent transfection experiments performed in duplicate. *p<0.05, compared with the basal activity of 3XIR2-TK promoter (4B), 3XIR2-TK (4C), or 3XDR4-TK (4D).