Figure 1.
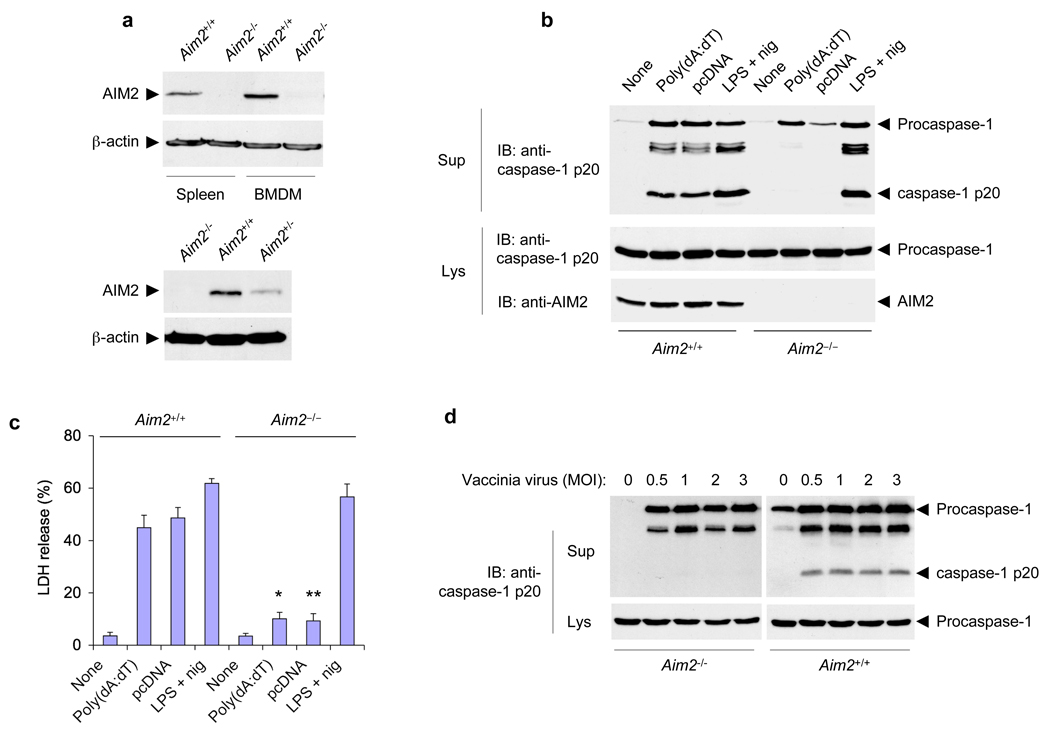
Disruption of mouse Aim2 abolishes activation of the inflammasome by cytoplasmic DNA and vaccinia virus. (a) Immunoblot analysis of the expression of AIM2 in spleens and BMDMs from Aim2+/+ and Aim2−/− littermates (top) and in spleens from Aim2−/−, Aim2+/+ and Aim2+/− mice (bottom), assessed with an antibody specific for mouse AIM2. β-actin serves as a loading control. (b) Immunoblot (IB) analysis of mouse procaspase-1, caspase-1 (p20 subunit) and/or AIM2 in culture supernatants (Sup) and lysates (Lys) of Aim2+/+ and Aim2−/− BMDMs left untreated (None) or transfected with the synthetic DNA poly(dA:dT) or plasmid DNA (pcDNA), or treated for 5 h with LPS (500 ng/ml) followed by nigericin (2.5 µM) for 45 min (LPS + nig), assessed with monoclonal antibody to mouse caspase-1 p20 (anti-p20). (c) Release of LDH into culture supernatants of the BMDMs described in b, presented relative to the total cellular LDH content. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01, Aim2+/+ versus Aim2−/− (Student’s t-test). (d) Immunoblot analysis of mouse procaspase-1 and caspase-1 in culture supernatants and lysates of mouse Aim2−/− and Aim2+/+ BMDMs infected for 18 h with vaccinia virus (multiplicity of infection (MOI), above lanes). Data are representative of at least three experiments (mean and s.d. in c).