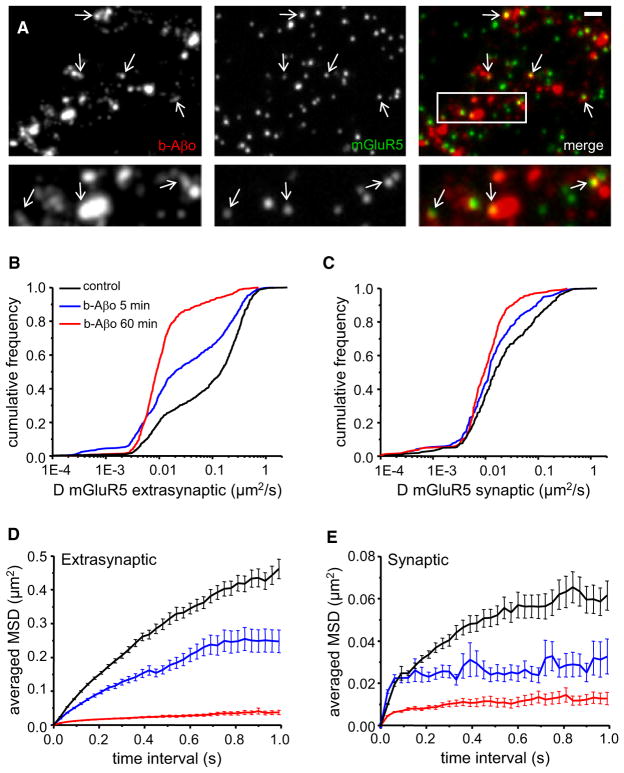
Figure 5. Aβ Oligomers Decrease mGluR5 Lateral Diffusion.
(A) Labeling of b-Aβo (left) and mGluR5 (center) and merging of both (right) in living neurons. Cells were incubated first with b-Aβo for 60 min (500 nM) and then with anti-mGluR5 (10 min). Arrows indicate spots of mGluR5 (green) colocalized with b-Aβo (red). (Bottom) Higher magnification of the area indicated by the white rectangle. Bar: 1 μm (top) or 0.5 μm (bottom).
(B and C) Diffusion coefficients D for QD-mGluR5 trajectories on extrasynaptic (B) and synaptic (C) membranes in control cells (black) or after application of Aβo (b-Aβo; 500 nM) for 5 (blue) or 60 (red) min.
(D and E) Averaged MSD (mean ± SEM) plots of the same trajectories analyzed in (B) and (C) at extrasynaptic areas (D) and at synapses (E). Same color coding as in (B) and (C). Note that the amplitude of the effects depends on the duration of application.