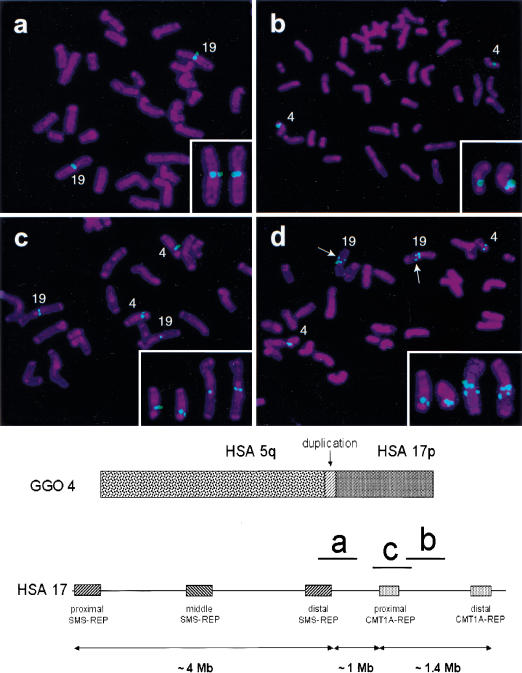
Figure 1.
Gorilla metaphase chromosomes after hybridization with human BAC clones. Below is shown gorilla chromosome 4 (GGO 4), syntenic to human chromosomes 5 and 17. The vertical arrow indicates the ∼250 kb genomic duplication, originating from the GGO 19 segment, syntenic to human chromosome, (HSA) 17p12. Smith-Magenis syndrome low-copy repeats, SMS-REPs, and Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A low copy repeats, CMT1A-REPs, in the human chromosome 17p11.2p12 region are shown (telomere to right of figure) with the relative physical position of three BAC clones used in the FISH analysis that is shown above. (a) CTD-3157E16 (HSA 17p12), located proximal to the translocation breakpoint. (b) RP11–726O12 (HSA 17p12), located distal to the translocation breakpoint. (c) RP11-385D13 (HSA 17p12, proximal CMT1A-REP), spans the translocation breakpoint and includes the genomic duplication in gorilla. (d) CTC-428H11 (HSA 5q13.3) spans the breakpoint. Arrows within the FISH picture indicate an additional hybridization signal, which is also located on the long arm of GGO 19. This apparent duplication is located distal to the evolutionary breakpoint identified in this study. Small panels in the lower right corners demonstrate only the gorilla chromosomes 4 and 19 with positive probe hybridization signals.