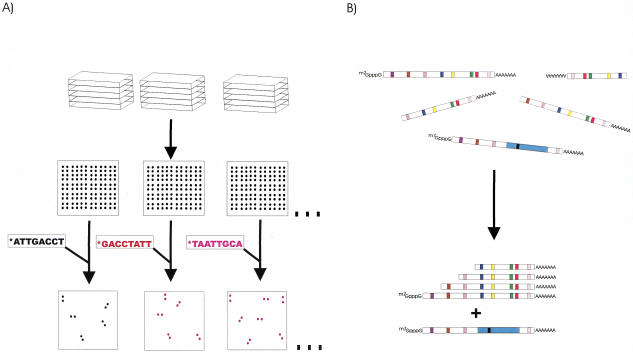
Figure 1.
Oligofingerprint (OFP) analysis. (A) Inserts from a gridded library are PCR amplified, and identical arrays are generated by spotting the amplicons. The arrays are sequentially probed with 33P-labeled, computer-selected, 8-mer oligonucleotides under high stringency conditions. In each hybridization, 5%–25% of the clones will be positive in each hybridization. (B) After image analysis quantifies the hybridization signals for each of the spots, a sequence fingerprint is generated for each clone based on which probe sequences are present and which are absent. Clustering algorithms then can group clones with significantly similar fingerprints (from the same transcript) together. cDNAs from the same gene, but different splice forms should be identifiable because they can give different fingerprints even if they share the same end sequences.