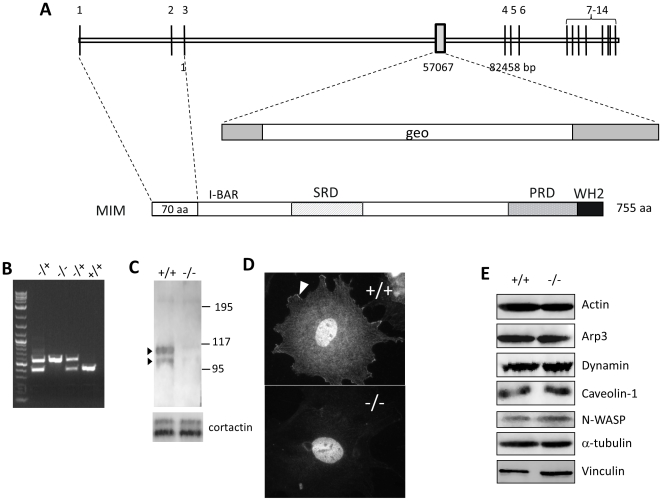
Figure 1. Preparation of MIM knockout mice.
(A) schematic illustration of the genomic structure of the murine MIM gene. The trapping vector, which carries a gal-neo (geo) fusion gene, targeted at the position corresponding to the nucleotide 57,067 in the third intron. (B) Genotyping of MIM knockout mice by PCR with the primers flanking the trapping vector. The top band (625 bp) indicates the mutant allele, and the lower band (400 bp) indicates the wild-type allele. (C) Western blot analysis of MEFs using MIM antibody, which detected a MIM characteristic duplex of p115 and p100 in the lysate of the MIM+/+ cells. The same membrane was re-blotted with cortactin antibody for the loading control (the lower panel). (D) Immunostaining of a MEF cell using MIM antibody. The arrow head indicates a representative lamellipodia staining. The nuclear staining was likely non-specific and observed with both MIM−/− and MIM+/+ cells. (E) Expression of several cortical proteins in MIM+/+ and MIM−/− MEFs.