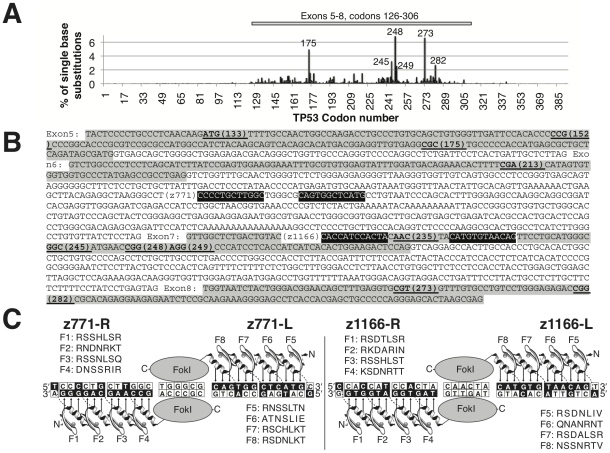
Figure 1. Zinc finger nucleases for the human p53 gene.
(A) Mutation hotspots in somatic cancers from the IARC TP53 Mutation Database R13. (B) Exons 5–8 from the p53 gene (Human Genome: NW_001838403) are highlighted in grey and contain nearly all mutation hotspots (underlined black; codon number in brackets). ZFN binding sites are highlighted in black with white letters. (C) Canonical model of designed zinc finger nucleases (z771 and z1166) against two target sites in the p53 gene. Arrows indicate possible base contacts. Zinc finger alpha helix sequences, involved in DNA recognition, are indicated (F1, Finger 1, etc.).