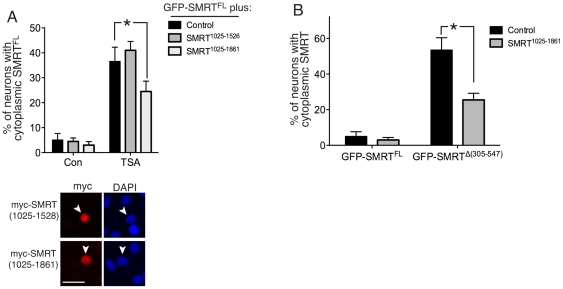
Figure 4. Over-expression of the RD4 region of SMRT inhibits HDAC inhibition-mediated SMRT export.
A) Upper: Over-expression of RD4 inhibits TSA-mediated nuclear export of SMRT. Neurons were transfected with GFP-SMRTFL plus an expression vector encoding the amino-acids 1025–1526 (RD3) or 1025–1861 (RD3–4) of SMRT or a control plasmid (encoding ß-globin). After 48 h neurons were treated with TSA and the subcellular localization of GFP-SMRTFL was analyzed. *p<0.05 (n = 4). Lower: Example pictures to illustrate the nuclear localization of SMRT1025–1526 and SMRT1025–1861. Neurons were transfected with plasmids encoding myc-tagged SMRT1025–1526 or SMRT1025–1861. After 48 h the localization of these portions of SMRT was analysed by immunofluorescence using an anti-myc antibody. Arrows point to a transfected cell in each case. B) Over-expression of the RD4 region partially reverses the cytoplasmic redistribution of SMRT caused by deletion of the DAD. Neurons were co-transfected with GFP-SMRTFL or SMRTΔ(305–547) with an expression vector encoding the amino acids 1025–1861 of SMRT or a control plasmid (encoding ß-globin) as indicated. After 48 h the cellular localization of SMRT and SMRTΔ(305–547) was analyzed. *p<0.05 (n = 3).