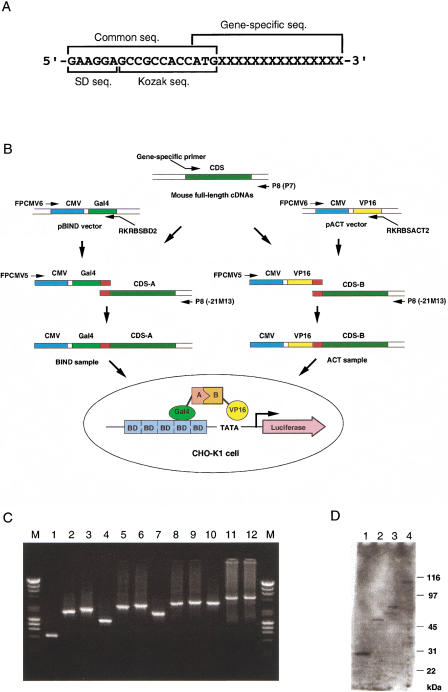
Figure 1.
Strategy for the high-throughput in vivo assay. (A) Design of the gene-specific forward primers. Each gene-specific forward primer was designed to anneal just downstream of the predicted initiation ATG of the gene. Each gene-specific forward primer has a common sequence that is used as a margin to connect the cDNA with other DNA sequences. The common sequence consists of the Shine-Dalgarno (SD) sequence for a prokaryotic ribosome-binding site, GAAGGA, and the Kozak consensus sequence for a eukaryotic translation initiation site, GCCGCCACCATG. (B) Schematic representation of the sample preparation and assay methods. (Thin arrows) PCR primers used; (red boxes) the common sequence region. The assay was performed based on the mammalian two-hybrid system. The pG5luc vector contains five Gal4 binding sites (BD) and a minimal TATA box, both of which are upstream of the luciferase gene; interaction between the BIND and ACT fusion proteins increases luciferase expression. (CDS) Protein coding sequence; (CMV) human cytomegalo virus immediate early promoter; (Gal4) yeast Gal4 DNA-binding domain; (VP16) herpes virus VP16 transcriptional-activation domain. (C) Agarose gel electrophoresis of the PCR-mediated constructs from various lengths of cDNAs. The constructs were prepared by two steps of PCR as described in the Methods. Two microliters of the first PCR products, BIND samples, and ACT samples were subjected to the 1% agarose gel in this order. A mixture of 250 ng of λ-HindIII and 250 ng of φX174-HaeIII was used as the size marker (M). Clone ID of each cDNA and the size of the first PCR product calculated from the nucleotide sequences were as follows: (lanes 1–3) 2010004E10, 0.6 kb; (lanes 4–6) 2310016E22, 1.2 kb; (lanes 7–9) 2310009C19, 1.9 kb; (lanes 10–12) 4931412A05, 3.3 kb. (D) Expression of the fusion proteins from the PCR-mediated samples. The fusion proteins expressed from the BIND samples in C were detected by Western blotting analysis using a monoclonal antibody against the Gal4 DNA-binding domain. Clone ID of each BIND sample and the size of the fusion proteins calculated from the deduced amino acid sequences were as follows: (lane 1) 2010004E10, 30 kD; (lane 2) 2310016E22, 57 kD; (lane 3) 2310009C19, 72 kD; (lane 4) 4931412A05, 101 kD. The size of the fusion protein in lane 4 seemed to be slightly larger than the calculated size. It is unclear whether it may be because of the posttranslational modifications.