Figure 4.
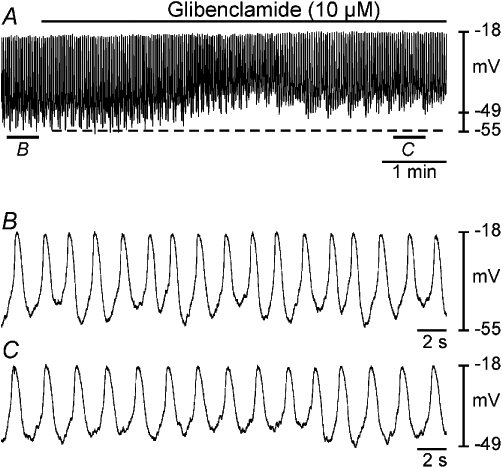
Effects of glibenclamide on slow wave activity. Intracellular microelectrode recordings (A–C) show the effects of the KATP channel antagonist glibenclamide (10 µM) on oviduct slow wave activity. (A) A period of control slow wave activity followed by application of glibenclamide (black bar). (B and C) Expanded time scales of the sections indicated in (A). Glibenclamide caused membrane depolarization (dashed line), increased slow wave frequency, decreased slow wave amplitude and reduced rate of rise of the upstroke phase of slow waves.
