Figure 4.
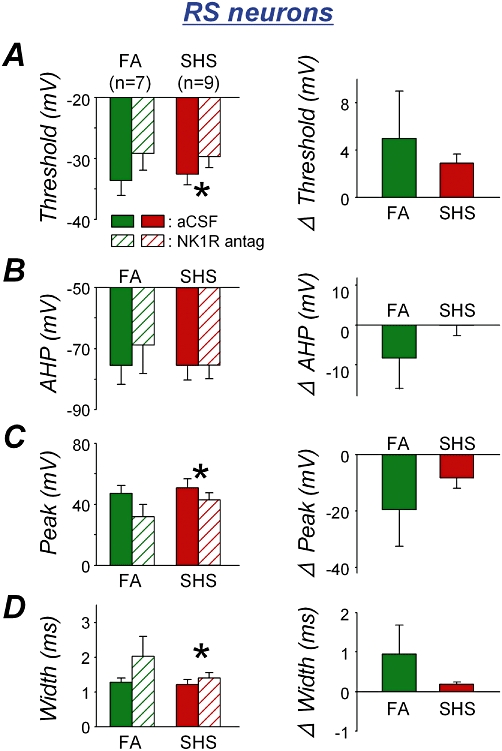
NK1 receptor antagonist effects (left panel) and their comparison between exposure groups (right panel) on action potential characteristics in rapid-onset spiking (RS) neurons. A. Action potential (AP) threshold. The NK1 receptor antagonist significantly increased AP threshold in second-hand tobacco smoke (SHS) exposure group (*P = 0.008) but not in filtered air (FA) exposure group (P = 0.205) (left). The antagonist effects between exposure groups were not different (P = 0.279) (right). B. Afterhyperpolarization (AHP). The antagonist did not change AHP in either exposure group (P > 0.05) (left). The antagonist effects between exposure groups were not different (P = 0.140) (right). C. AP peak amplitude. The antagonist significantly reduced the AP peak amplitude in SHS but not in the FA exposure group (*P = 0.036 and P = 0.078 respectively) (left). The antagonist effects between exposure groups were not significantly different (P = 0.177) (right). D. AP width. The antagonist significantly prolonged AP width in SHS exposure group (*P = 0.011) but not in FA exposure group (P = 0.103) (left). The antagonist effects between exposure groups were not significantly different (P = 0.115) (right). aCSF, artificial cerebrospinal fluid.
