Fig. 3.
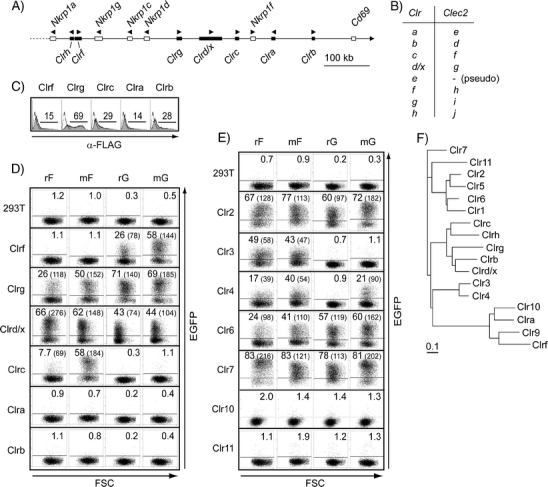
Rat and mouse NKR-P1F and NKR-P1G reporters show overlapping specificities against a panel of Clr transfectants. a Schematic map of the centromeric part of the mouse NKC based on a C57BL/6J chromosome 6 genomic contig (NT_039353.7). The distance from Nkrp1a to Clrb is approximately 577 k. Only functional genes are shown; the predicted mRNA sequence of Clrh has not been confirmed. b The Clr nomenclature has previously been confused by erroneously assembled genomic clones. A conversion table of the suggested Clr and Clec2 nomenclature is shown. c Surface expression of the FLAG-tagged mouse Clr molecules (filled histograms) was verified by staining with mAb M2 and flow cytometry, and staining of untransfected 293T control cells is shown as unfilled histograms. An untagged version of Clrd/x was tested in a separate set of experiments. Reporter cells (r rat and m mouse) were co-incubated overnight with 293T stimulator cells transiently transfected with the indicated d mouse and e rat Clr molecules and stimulation measured as an EGFP signal by flow cytometry. Numbers represent percentage and MFI values (in parenthesis) of positive cells. Transfection efficiency of the rat Clr constructs was verified by EYFP staining (data not shown). Clr10 was tested in a separate set of experiments. One representative out of three to five experiments is shown. f Phylogenetic tree based on the extracellular aa sequence of various mouse and rat Clr molecules, accession numbers given in parenthesis: Clr1 (NP_001019508), Clr2 (ABX54835), Clr3 (ACJ23591), Clr4 (ACJ23593), Clr5 (ABO15828), Clr6 (ACJ23590), Clr7 (ABX54838), Clr9 (XP_232399), Clr10 (ACJ23592), Clr11 (ABX54837), Clra (AAL37200), Clrb (AAK70357), Clrc (ADX42723), Clrd/x (also called ocilrp1, BAE23491), Clrf (AAK70358), Clrg (AAK70359), Clrh (XP_001480526)
