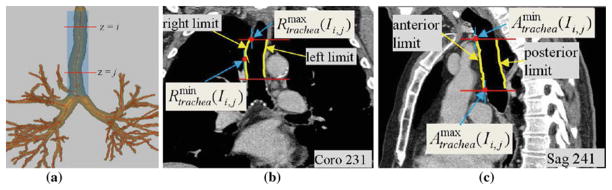
Fig. 3.
Example landmark definitions for the right, left, anterior, and posterior limits of a structure computed over a range of 2D transverse-plane sections I (·, ·, z), i ≤ z ≤ j. This example focuses on the trachea. All 2D section views in this figure and the figures to follow use the mediastinal window [window width = 400, window level = −160] for display, unless otherwise stated. a Depiction of transverse-plane sections passing through the trachea between z = i and z = j. b 2D coronal-plane section I (x, ·, ·) at x = 231 depicting the right and left surfaces of the trachea between i ≤ z ≤ j (yellow); gives the minimum x value of the right tracheal surface points (middle red dot), while gives the maximum x value of the right tratrachea surface points (upper red dot). c 2D sagittal-plane section I (·, y, ·) at y = 241 depicting the anterior and posterior surfaces of the trachea between i ≤ z ≤ j (yellow); gives the minimum y value of the anterior tracheal surface points (upper red dot), while gives the maximum y value of the anterior tracheal surface points (lower red dot)