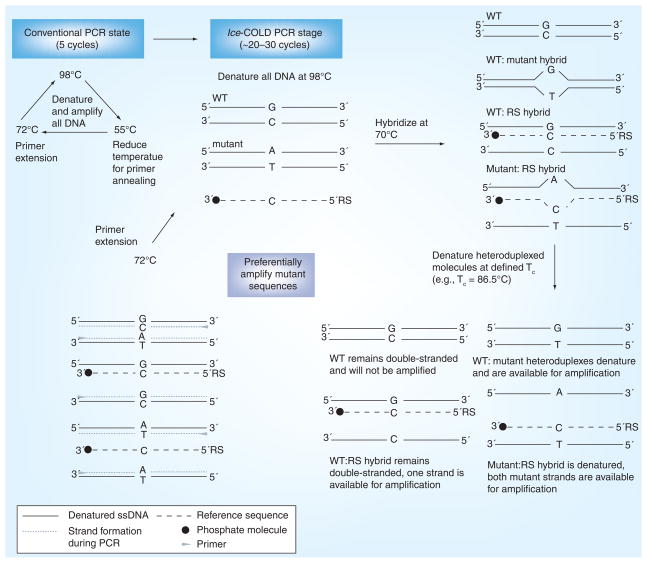
Figure 2. Ice-coamplification at lower denaturation temperature-PCR protocol schematic.
Ice-COLD-PCR has the potential to enrich all possible mutations and also provides a higher enrichment than full-COLD-PCR. Ice-COLD-PCR is performed in a nested format here (i.e., using a larger PCR amplicon as a template). An initial few rounds of nested conventional PCR are first applied to enable build-up of the target amplicon(s). After denaturation at approximately 98.0°C (or as defined by the polymerase system), the PCR amplicon(s) and the oligonucleotide reference sequence are hybridized at 70.0°C. Mutant-containing heteroduplexed molecules (mismatch-containing) will be denatured at the Tc, and preferentially enriched throughout the course of ice-COLD-PCR.
COLD: Coamplification at lower denaturation temperature; RS: Reference sequence; Tc: Critical denuration temperature; WT: Wild-type. Data from [28].