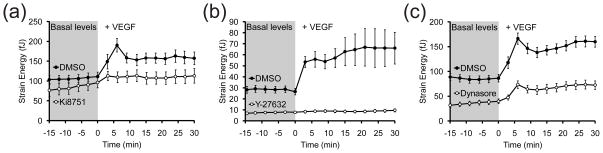
Figure 6. Effects of VEGFR2, ROCK and dynamin inhibition on the VEGF-induced contractile response.
(a) Time-series plot of the average strain energy of cells pre-treated with 10 μM Ki8751 (white circles) or DMSO (black circles) from t = −60 to 0 min and then stimulated with VEGF (50 ng/mL) immediately after t = 0 min. Data for each treatment condition is the average of n = 23 (Ki8751 + VEGF) and n = 47 (DMSO + VEGF) cells from one and two experiments, respectively. Error bars are ± SEM. (b) Time-series plot of the average strain energy of cells pre-treated with 25 μM Y-27632 (white circles) or DMSO (black circles) from t = −30 to 0 min and then stimulated with VEGF (50 ng/mL) immediately after t = 0 min. Data for each treatment condition is the average of n = 26 (Y-27632 + VEGF) and n = 58 (DMSO + VEGF) cells from two and four experiments, respectively. Error bars are ± SEM. (c) Time-series plot of the average strain energy of cells pre-treated with 30–50 μM Dynasore (white circles) or DMSO (black circles) from t = −60 to 0 min and then stimulated with VEGF (50 ng/mL) immediately after t = 0 min. Data for each treatment condition is the average of n = 95 (Dynasore + VEGF) and n = 96 (DMSO + VEGF) cells from four experiments each. Error bars are ± SEM.