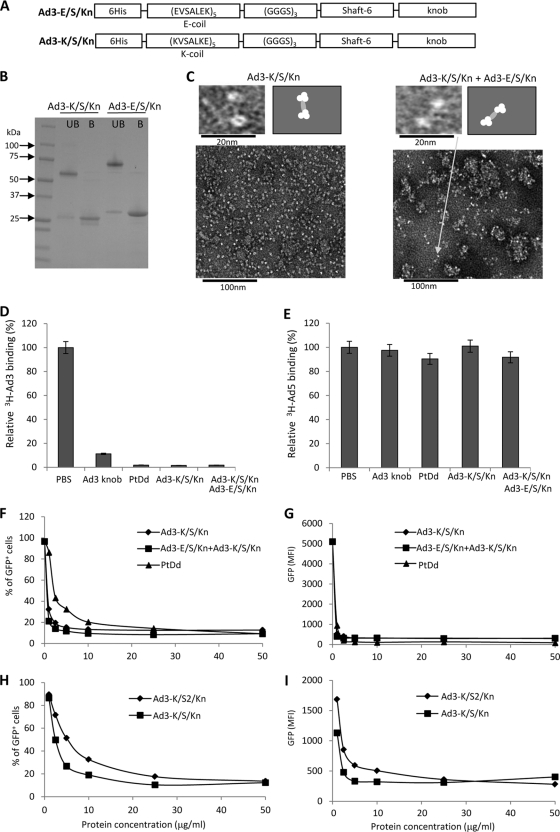
Fig. 4.
Analysis of dimeric fiber knobs containing only one shaft motif. (A) Schematic structure of recombinant Ad3 fiber knob proteins Ad3-K/S/Kn and Ad3-E/S/Kn. The theoretical molecular mass of each fiber knob trimer is ∼60 kDa. (B) Coomassie blue-stained gel. Samples were run on a 4 to 15% gradient polyacrylamide gel in Tris–glycine–0.1% SDS buffer. UB, unboiled samples; B, boiled samples. Note that boiling in Laemmli buffer disrupts the trimeric protein structures, resulting in ∼25-kDa fiber knob monomers. (C) Negative-stain electron microscopy of purified Ad3-K/S/Kn and Ad3-K/S/Kn mixed with Ad3-E/S/Kn. The upper left image shows fiber knob dimers in both preparations. Note that the fiber knob itself is a trimer. The lower images show aggregates that contain more than two fiber knobs. The right panels show schematic drawings of the photographs. (D) Blocking of 3H-Ad3 attachment by recombinant Ad3 fiber knobs or PtDd. Ad attachment to cells incubated with PBS was taken as 100%. n = 3. (E) Blocking of 3H-Ad5 attachment by recombinant Ad3 fiber knobs or PtDd. Ad attachment to cells incubated with PBS was taken as 100%. n = 3. (F and G) Competition of Ad3-GFP transduction. HeLa cells were incubated with increasing concentrations of fiber knobs or PtDd for 60 min and then infected with Ad3-GFP at an MOI of 100 PFU/cell for 60 min, after which the viruses were removed and new medium added. GFP fluorescence was measured 18 h later. n = 3. Shown are average values of percent GFP-positive cells (F) and mean GFP fluorescence (G). The SD were less than 10% for all samples. (H and I) The same study as that described for panels F and G was performed but with Ad3-K/S/Kn and the fiber knobs with two shaft motifs, Ad3-K/S2/Kn.