Figure 2. Comparison of riboswitches and proteins that bind a common ligand.
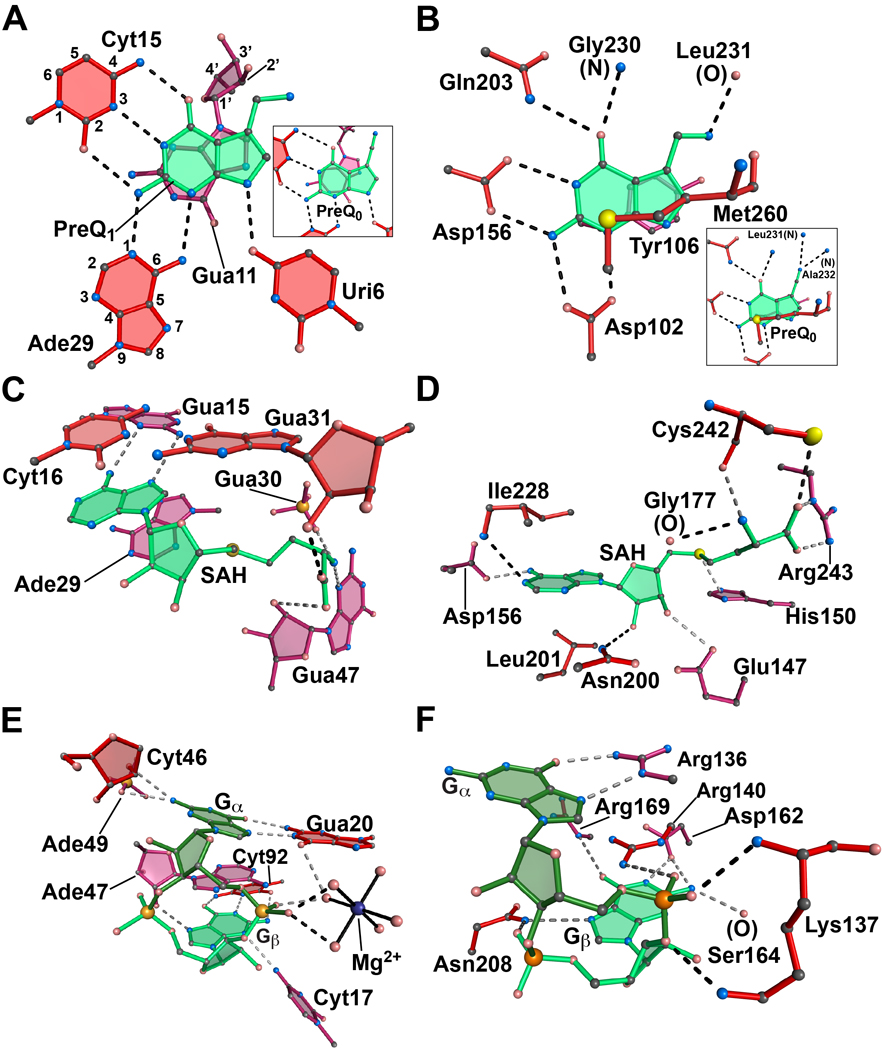
(A) The metabolite-binding site of the class I preQ1 riboswitch in complex with preQ1 from T. tengcongensis. Inset: The same aptamer in complex with preQ0. The respective PDB codes are 3Q50 and 3GCA. The atoms have been numbered for representative purine and pyrimidine bases according to IUPAC-IUB nomenclature. (B) The active site of the enzyme tRNA-guanine transglycosylase (TGTase) from Z. mobilis in complex with preQ1. Inset: The same enzyme in complex with preQ0. The respective PDB codes are 1P0E and 1P0B. (C) The metabolite-binding site of the SAH riboswitch from R. solanacearum in complex with SAH. The PDB code is 3NPQ. (D) The active site of the BchU methyltransferase from C. tepidum bound to SAH. The PDB code is 1X1B. (E) The c-di-GMP riboswitch aptamer from Vibrio cholerae in complex with the second messenger c-di-GMP. The PDB code is 3MXH. A hydrated Mg2+ is shown (blue) with solid lines drawn to waters (pink spheres) in the inner coordination sphere. (F) The PilZ domain (VCA0042) from Vibrio cholerae in complex with c-di-GMP. The PDB code is 2RDE. All ligands are depicted in shades of green. Nucleotides and amino acids of the binding pockets are shown in shades of burgundy to indicate depth; red is the topmost layer and crimson is at the bottom. Dashed lines signify putative hydrogen bonds.
