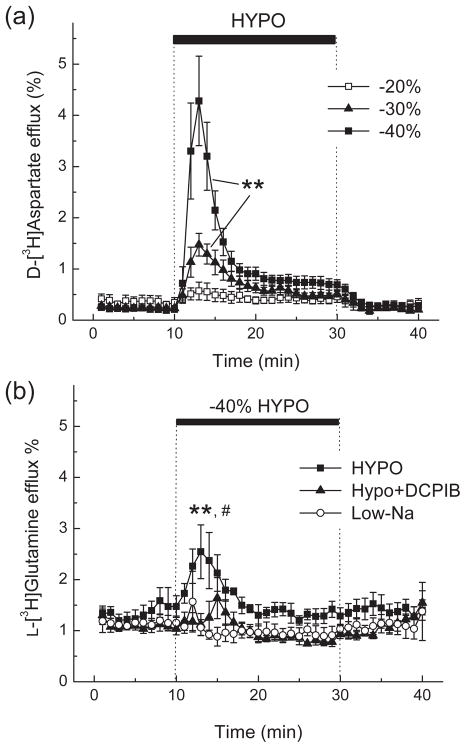
Fig. 2. Hypoosmotic medium strongly stimulates glutamate (D-[3H]aspartate) release and increases the release of L-[3H]glutamine in primary rat astrocytes.
(a) Dose dependence of osmolarity effects on the release of D-[3H]aspartate from astrocyte cultures. Cells were preloaded for 30 min with D-[3H]aspartate and then perfused with isoosmotic (basal) or hypoosmotic media (HYPO) in which osmolarity was reduced by 20, 30, or 40%. Data are the mean values ±SE of 4–5 experiments. **p<0.01 HYPO vs. basal release, repeated measures ANOVA. (b) Effect of 40% HYPO, isoosmotic low [NaCl] (Low-Na) medium, and the VRAC blocker DCPIB on L-[3H]glutamine release from primary astrocytes. For each experiment, cells were preincubated with the glutaminase inhibitor 1 mM DON and then preloaded for 30 min with L-[3H]glutamine. Data are the means ±SE of 4–5 experiments. **p<0.01 HYPO vs. Low-Na, #p<0.05, HYPO vs. HYPO+DCPIB.