Figure 1.
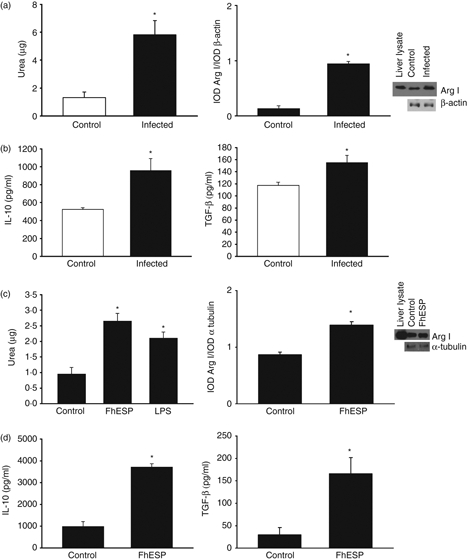
Products from Fasciola hepatica are able to induce immunomodulatory effects on peritoneal macrophages (pMΦ) in the early stage of infection as well as after in vitro stimulation. Expression levels of Arginase I (Arg I) by Western blot and arginase activity in pMΦ derived from infected BALB/c mice, 48 hr after metacercariae challenge and further cultivation for 48 hr, as well as in naive mice derived pMΦ stimulated with F. hepatica excretory–secretory products (FhESP; 20 μg/ml) for 48 hr (a, d). Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and interleukin-10 (IL-10) levels were measured by ELISAs in culture supernatants in the respective pMΦ of the ex vivo (b) and in vitro (d) experiments. In the infection experiment, four mice/group were analysed. Data are mean ± SEM of three independent experiments, analysed in triplicate. *P<0·05 respect to pMΦ from non-infected mice (a–c) or pMΦ in medium alone (c–d).
