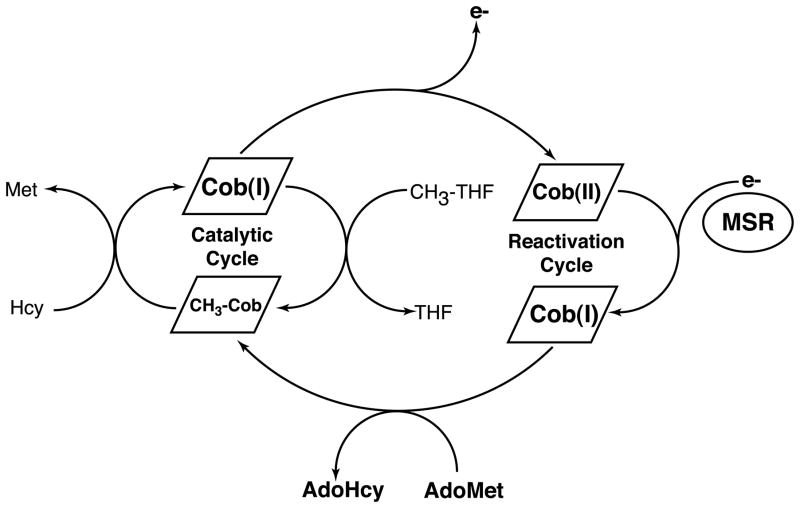
Figure 4.
Reactions catalyzed by mammalian methionine synthase. During catalysis, the cobalamin cofactor of methionine synthase cycles between the methylcobalamin and cob(I)alamin forms, as the cofactor is alternately methylated by methyltetrahydrofolate (CH3-THF) and demethylated by homocysteine to form methionine. Cob(I)alamin is occasionally oxidized to form an inactive cob(II)alamin species; return of this species to the catalytic cycle requires a reductive remethylation of the cofactor in which an electron is provided by the auxiliary protein methionine synthase reductase (MSR) and a methyl group is provided by AdoMet, which is bound to the reactivation module of methionine synthase itself.