Figure 5.
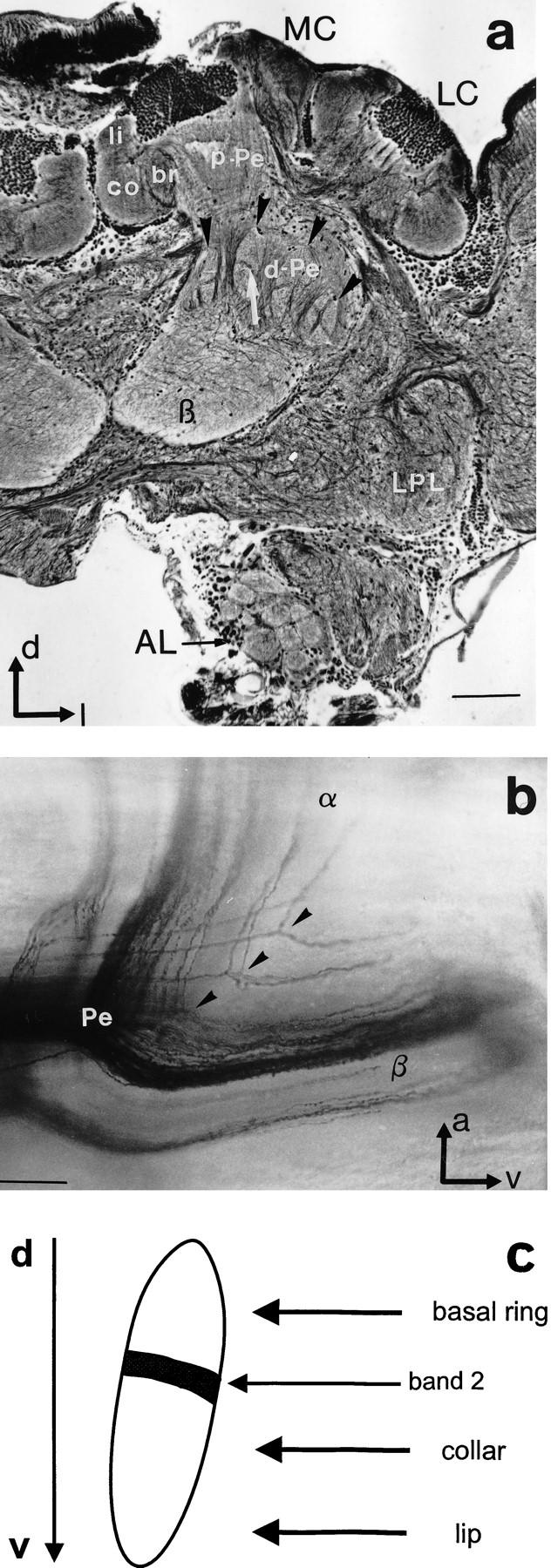
Structural organization of the MBs and Pe1 innervation. (a) Bodian staining reveals subcompartments of MBs at a depth of ∼250 μm (frontal view). The calyces (MC, LC) are composed of ring neuropils, lip, collar, and basal ring (li, co, br). Axonal projections of the Kenyon cells form the layered proximal peduncle (p-Pe). Axons in the distal peduncle (d-Pe) split into collaterals more distal to the calyces. The finger-like structures (black arrowheads) are collaterals that form more anteriorly the α-lobe, which extends into more frontal sections. Longitudinal areas extend into the β-lobe (β). Note the banding pattern in the vertical structures (arrow). (AL) Antennal lobe; (LPL) lateral protocerebral lobe. Scale, 100 μm. (d) Dorsal; (l) lateral. (b) Sagittal view of a Golgi–Collonier staining of Kenyon cell axon bundles at the splitting point [transition from peduncle (P) to α- and β-lobe, α and β]. Scale, 50 μm. (a) Anterior; (v) ventral. (c) Allocation of calycal subcompartments (basal ring, collar, and lip) to zones in the peduncle. The black bar in the finger-like structure represents the thin band shown in a (arrow).
