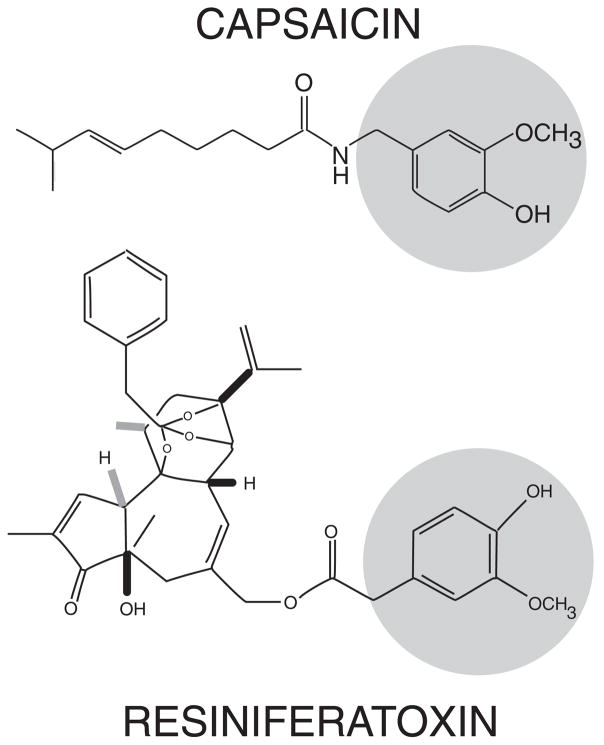
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of capsaicin (top) and resiniferatoxin (RTX) (bottom) illustrating common active moieties including –methoxy and hydroxyl groups (circled). Although both function as agonists at the TRPV1 receptor, RTX has higher potency and a characteristically slow but persistent activation.