Figure 2.
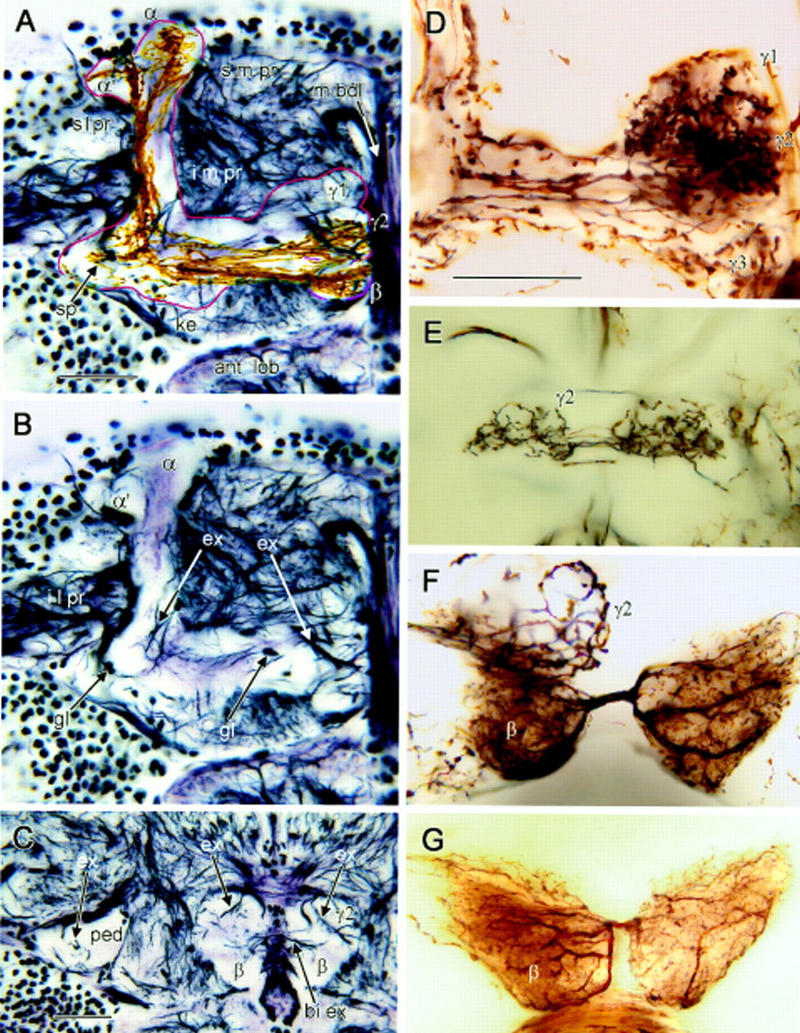
Bodian and Golgi stained mushroom bodies. (A–C) Bodian-stained frontal sections showing one mushroom body’s medial and vertical lobes (A,B), and pedunculus cross section (C). (s m pr) Superior medial protocerebrum, (s l pr) superior lateral protocerebrum, (i m pr) inferior medial protocerebrum, (i l pr) inferior lateral protocerebrum. (m bdl) Median bundle, (ant lob) antennal lobe. (A) Outline (red) indicates limits of mushroom body neuropil. The head of the γ lobe has three swellings (γ1–γ3 from dorsal to ventral; see also D). The middle swelling (γ2) lies more posterior to γ1 and γ3. The keel (ke) is a local swelling within the γ lobe, and the spur (sp) is the root swelling of γ. The β lobe lies ventroposterior to γ. Its terminal swelling bends downwards and situates behind γ3 and beneath γ2 (see also Fig. 4E). Note the taller, medially inclined α lobe and the lower, laterally bent α′ lobe. Golgi-impregnated Kenyon cell axons are superimposed against the Bodian stained lobes. Axons extending through γ have short branches to the spur (sp) and long collaterals to α′. Thinner, straighter axons in β have collaterals into α. (B) Profiles of extrinsic neurons within the root of the vertical lobe (left arrow ex) and the swellings of the γ lobe (right arrow ex). Argyrophilic extrinsic neuron profiles in the head of γ match profiles of Golgi-impregnated extrinsic neurons in Fig 3D, right. Glial cell bodies (gl) reside at the edges and within the mushroom body neuropil (montage of three optical sections). (C) Pedunculus cross section near its anterior end (ped) contains few argyrophilic extrinsic fibers (upper left, arrow ex). Extrinsic fibers (upper right, two arrows ex) connect the posteriormost γ lobe swelling (γ2) and surrounding neuropil. Processes linking the left and right β lobes (lower right, arrow bi ex) correspond to connections of bilateral extrinsic neurons in F, G, and Fig. 3G. (D) Three swellings of the γ lobe head. In this Golgi preparation γ3 receives a subset of Kenyon cell axons alone. The more dorsal γ1 and γ2 swellings show convergence of Kenyon cell axons and an afferent terminal. (E) Bilateral terminal of an afferent supplying γ2 (complete reconstruction; Fig. 3F). (F) Heterolateral extrinsic neuron dendrites connect terminal swellings of the β lobes (see Fig. 3G). A whorl of Kenyon cell axons is labeled in γ2. (G) Another preparation reveals the same type of extrinsic neuron as in F, suggesting morphological consistency in different individuals. Scale bar, 25 μm.
