Figure 6.
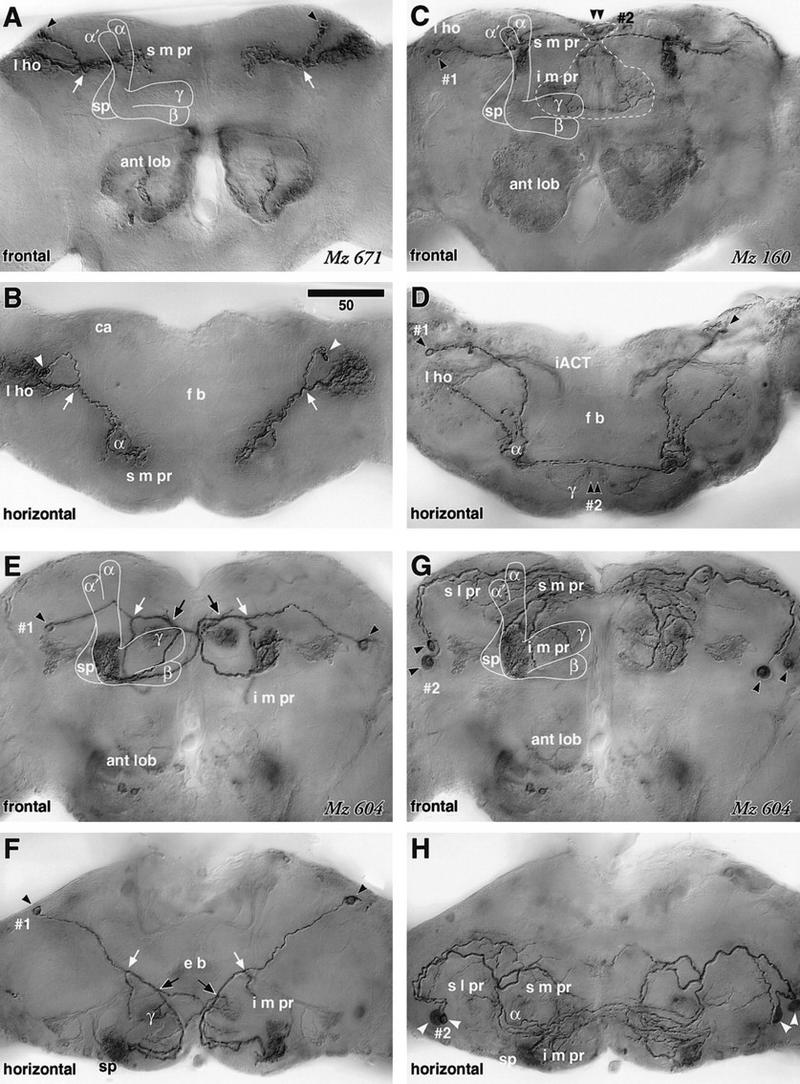
Extrinsic neurons connecting the mushroom body and lateral protocerebrum. A–D are digital camera-lucida montages of identical preparations viewed frontally (dorsal to the top) and horizontally (anterior to the bottom). E–H are each montages of the same preparation but tracing different neurons (1 and 2). (A,B) GAL4 enhancer-trap strain Mz 671 labels a pair of extrinsic neurons that connect the lateral horn (l ho) and the α lobe (diagram in Fig. 7G). The cell body lies in the posterior dorsal cortex (arrowhead), and the fiber bifurcates in the dorsal protocerebrum (arrow). Its lateral branch provides extensive arborizations in the lateral horn. The medial branch crosses the neuropil obliquely, circumvents the shaft of the α lobe, and arborizes around the shaft in the superior medial protocerebrum (s m pr). Some arborizations also invade the head of the α lobe. The neuron has presynaptic sites in the s m pr and lateral horn, but not in the α lobe head (see Fig. 7B). (C,D) Cell type (1) labeled by Mz 160, has its cell body in the posterior cortex (arrowhead, diagram in Fig. 7H). Its cell body fiber runs across the dorsal neuropil to project to the α lobe, where it forms an elaborate arborization in which n-syb GFP-staining demonstrates presynaptic sites (see Fig. 7D). The nearby s m pr is also invaded by processes, and a lateral branch projects to the lateral horn (l ho). Another branch projects to the contralateral α lobe head. (2) Cell type with cell bodies in the dorsal midline cortex (arrowhead) that sends fibers to the i m pr just above the γ lobes, but does not invade the mushroom body. (E,F) One of the cells labeled in Mz 604 (1) has its cell body in the posterior cortex (arrowheads) and projects through the inferior protocerebrum (diagram in Fig. 7I). It forms its first bifurcation (white arrow) lateral to the ellipsoid body (e b), sending a branch ventrally to the i m pr just above the ant lob. This is succeeded by a second bifurcation (black arrow) from which a branch crosses the midline and projects to the contralateral mushroom body’s spur (sp). The ipsilateral branch forms a small arborization in the posterior swelling of the γ lobe head, extends further in front of the γ lobe, and follows the contralateral projection of its opposite counterpart to form an extensive arborization within the root of the γ lobe, which contains numerous presynaptic sites (Fig. 7F). (G,H) Labeled cell type (2) that derives from two cell bodies in the anterior lateral cortex (arrowheads, diagram in Fig. 7J). The cell body fibers project along the perimeter of the s l pr, where they provide extensive branches along the surface of the s l pr, s m pr, and i m pr, and also invade the α lobe and the spur (sp). Scale = 50 μm.
