Figure 7.
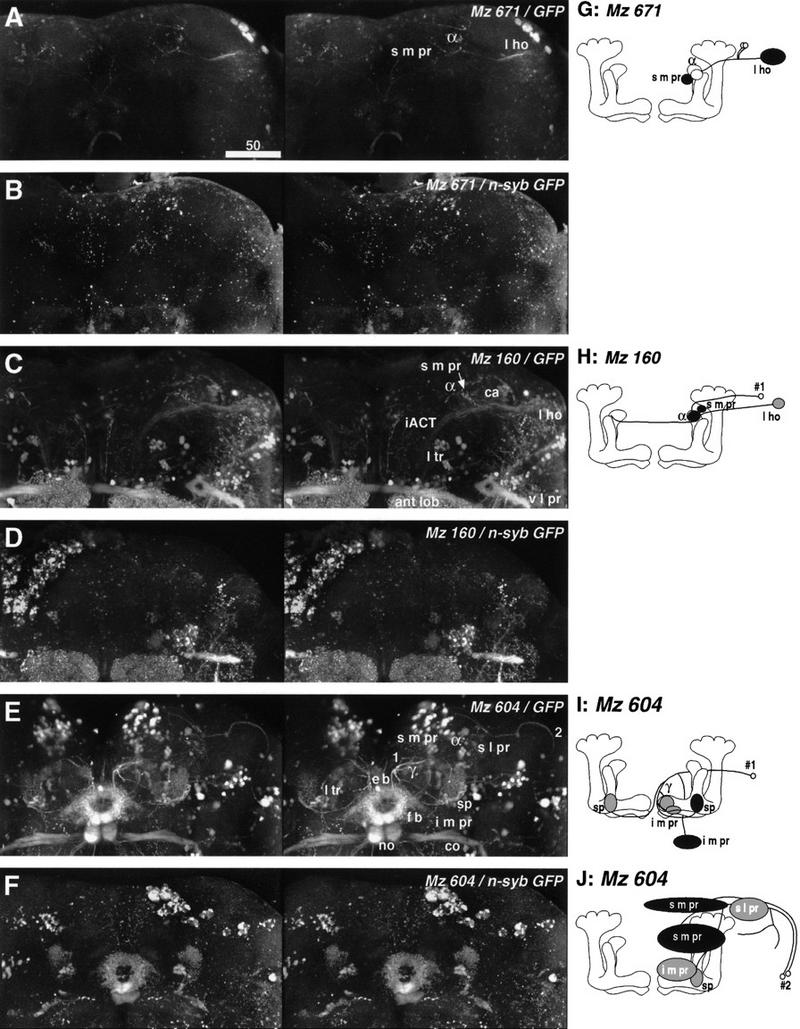
Stereographs and diagrams of the neurons shown in Fig. 6. A–F are three dimensional stereographs of reconstructions (frontal view) of cytoplasmic GFP (A,C,E) and presynaptic n-syb–GFP (B,D,F) labeling. (A) GFP staining of the line Mz 671 reveals the connection between the lateral horn (l ho) and the α lobe head as well as the surrounding s m pr (diagram in G, see also Fig. 6A,B). (B) Presynaptic sites are found in the s m pr, but not in the α lobe (confirmed by examining each confocal section). Very faint staining is also observed in the lateral horn. (C) Mz 160 labels another connection between the lateral horn (l ho) and the α lobe/s m pr (diagram in H, see also Fig. 6C,D). Also labeled are iACT neurons with arborizations in the antennal lobe (ant lob), calyx (ca), and lateral horn. Other labeling is in projections to the lateral triangle (l tr) of the central complex, commissures between the ventrolateral protocerebra (v l pr), and tracts connecting the v l pr and lateral horn. (D) Unlike Mz 671, the α lobe head of this extrinsic neuron possesses presynaptic sites (confirmed by examining each confocal section), suggesting that the α lobe receives afferents. Because of the staining of the iACT terminals, we could not confirm whether this neuron also has presynaptic sites in the lateral horn. (E) Line Mz 604 labels two types of extrinsic neurons (1 and 2, diagram in I and J, see also Fig. 6E–H). Also labeled are commissures (co) connecting antennal mechanosensory regions, as well as projections from cells in the posterior cortex to the fan-shaped body (f b), ellipsoid body (e b), noduli (no), and from cells in the anterior cortex to the lateral triangle (l tr). (F) Presynaptic sites of neuron 1 are found in the root of the γ lobe and in the i m pr. Those of neuron 2 can be seen in the s m pr near the midline and in the s m pr in front of the shaft of the vertical lobe. G–J are diagrams of extrinsic neurons described in Figs. 6 and 7. Labels as in Fig. 5. The white ellipsoid denotes the area confirmed to be free from presynaptic sites.
