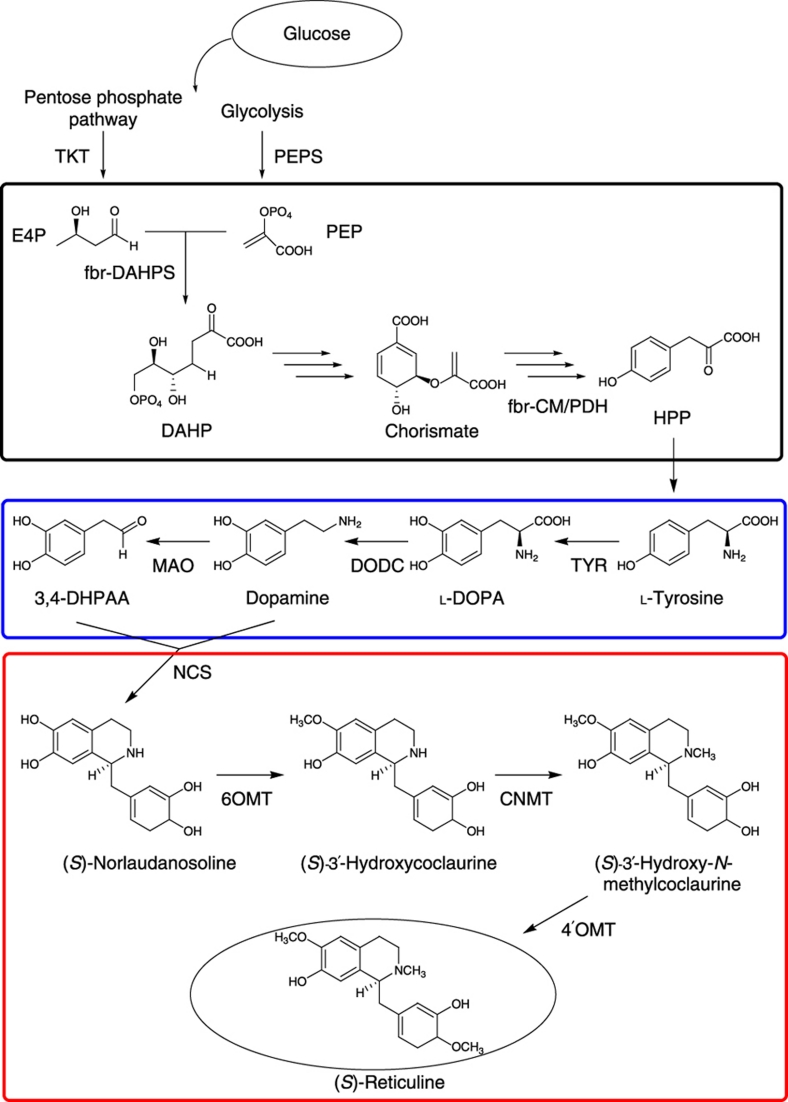
Figure 1. Bacterial BIA biosynthetic pathway constructed in Escherichia coli cells.
For L-tyrosine over-production, four enzymes (TKT, PEPS, fbr-DAHPS and fbr-CM/PDH) are overexpressed. Black box indicates the common aromatic pathway. The tailor-made biosynthetic pathway (blue) consisted of TYR, DODC and MAO. The plant biosynthetic pathway (red) was modified to circumvent the CYP80B reaction. CNMT, coclaurine-N-methyltransferase of Coptis japonica (GenBank accession number AB061863); DAHPS, 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase (aroGfbr, GenBank accession number J01591); DODC, DOPA decarboxylase of Pseudomonas putida (GenBank accession number AE015451); E4P, erythrose-4-phosphate; fbr, feedback-inhibition-resistant; fbr-CM/PDH, fbr-chorismate mutase/prephenate dehydrogenase (tyrAfbr, GenBank accession number M10431); HPP, 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate; MAO, monoamine oxidase of Micrococcus luteus (GenBank accession number AB010716); NCS, norcoclaurine synthetase of C. japonica (GenBank accession number AB267399); PEPS, phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) synthetase (ppsA, GenBank accession number X59381); TKT, transketolase (tktA, GenBank accession number X68025); TYR, tyrosinase of Streptomyces castaneoglobisporus (ScTYR containing tyrosinase and its adaptor protein, ORF378, GenBank accession numbers AY254101 and AY254102) or tyrosinase of Ralstonia solanacearum (RsTYR, Rcs0337, GenBank accession number AL646052); 3,4-DHPAA, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde; 6OMT, norcoclaurine 6-O-methyltransferase of C. japonica (GenBank accession number D29811); 4′OMT, 3′-hydroxy-N-methylcoclaurine 4′-O-methyltransferase of C. japonica (GenBank accession number D29812).