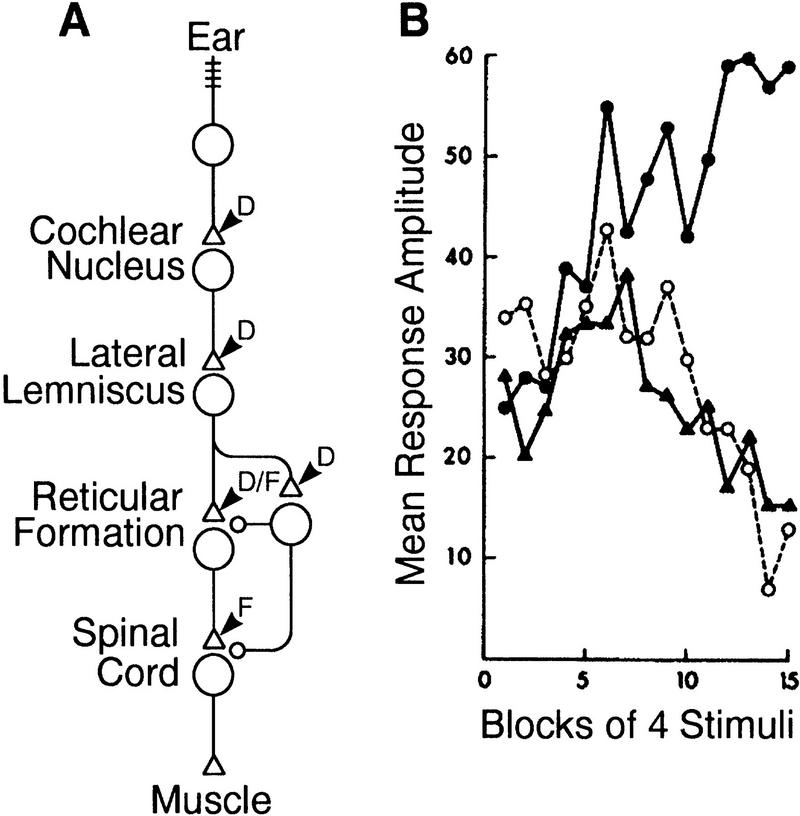
Figure 3.
Acoustic startle reflex in the rat. (A) Neural circuitry mediating the acoustic startle reflex. The circuit diagram shows the S-R pathway (cells with triangular synapses) and modulatory system (cell with circular synapses). (B) Effects of stimulating at different positions along the S-R pathway: acoustic stimulation (▴), electrical stimulation of the cochlear nucleus (○), and electrical stimulation of the reticular formation (•). Response amplitude is measured as the velocity of cage displacement caused by the startle response. Notice that the first two forms of stimulation cause canonical dual-process learning, whereas the third form of stimulation elicits only sensitization. The interpretation of these results in terms of the location of expression of depression (D) and facilitation (F) within the S-R pathway (i.e., at triangular synapses) is shown in A. B is reprinted, with permission, from Davis et al. (1982b). Copyright 1982 by the American Association for the Advancement of Science.