Figure 1.
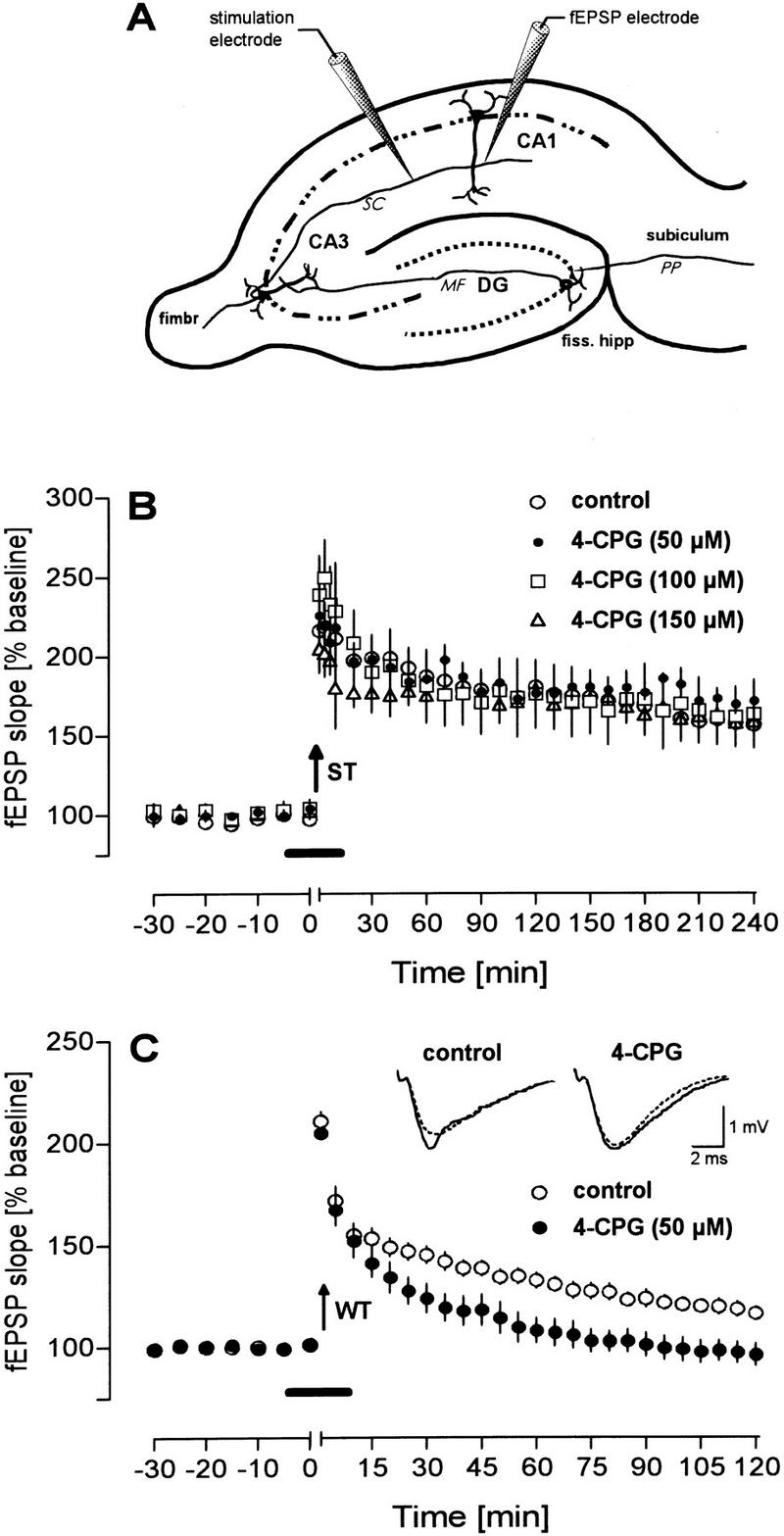
Under in vitro conditions, the mGluR group I antagonist 4-CPG impairs LTP induced by weak tetanization (WT) but not by strong tetanization (ST). (A) Scheme of the placement of recording electrodes in the CA1 region. (B) 4-CPG applied in increasing concentrations does not impair a potentiation induced by a strong tetanization paradigm (ST; 10 bursts of four stimuli at 100 Hz, separated by 200 msec) but was effective (C) if a weak tetanization protocol (WT; 100 Hz, 400-msec duration) was used to generate LTP. Analog traces depict typical responses taken immediately before tetanization (broken line) and 60 min thereafter (solid line). Arrows indicate the time of tetanization and horizontal bars indicate the bath application of 4-CPG.
