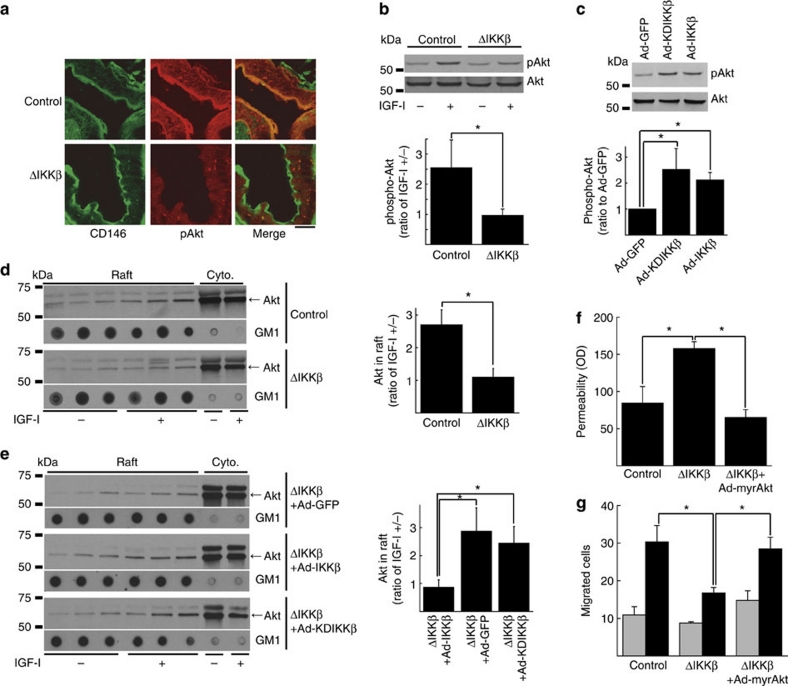
Figure 4. Akt phosphorylation and localization in IKKβ-manipulated endothelial cells in vivo and in vitro.
(a) Confocal microscopy images of endothelial cells in IKKβΔEC mice immunostained with antibody for CD146 and pAkt. Scale bar: 20 μm. (b) Representative immunoblots for pAkt and Akt in IKKβ-deleted endothelial cells treated with/without IGF-I and its cumulative quantitative densitometry data±s.d. from three independent experiments (*P<0.05 in two-sided Student's t-test). (c) Representative immunoblots for pAkt and Akt in endothelial cells overexpressed with WT- or KD-IKKβ and its cumulative quantitative densitometry data±s.d. from three independent experiments (*P<0.05 in two-sided Student's t-test). (d) Representative Akt immunoblots of fractions from sucrose gradient centrifugation of IKKβ-deleted endothelial cells treated with/without IGF-I and its cumulative quantitative densitometry data±s.e. from three independent experiments (*P<0.05 in two-sided Student's t-test). Ganglioside GM1 is marker for lipid raft fractions. (e) Representative Akt immunoblots of fractions from sucrose gradient centrifugation of IKKβ-deleted endothelial cells expressed with either WT- or KD-IKKβ treated with/without IGF-I and its cumulative quantitative densitometry data±s.e. (n=5 for ΔIKKβ+Ad-GFP; n=3 for ΔIKKβ+Ad-IKKβ; n=5 for ΔIKKβ+Ad-KDIKKβ; *P<0.05 in two-sided Student's t-test). Ganglioside GM1 is marker for lipid raft fractions. (f, g) In vitro permeability (f) and migration to VEGF (g) in endothelial cells in which IKKβ is deleted or myr-Akt is expressed. Gray bars: VEGF (−), black bars: VEGF (+) for (g). Each panel is cumulative data±s.e. from three independent experiments (*P<0.05 in two-sided Student's t-test).