Figure 2.
Identification of Mutations in PLCD1 and Function of Mutant PLCD1
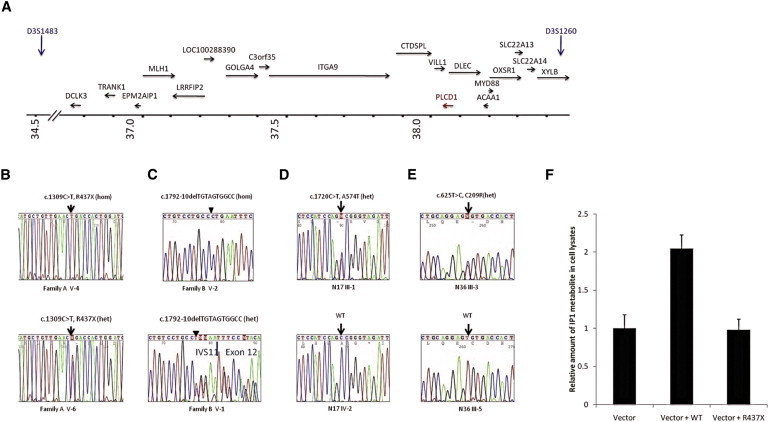
(A) Schematic representation of the candidate region harboring PLCD1. Arrows indicate the position and the direction of transcription of genes in the region. FCHP, LOC100130503, ARPP21, and STAC are located upstream of the region shown where the axis has been truncated.
(B and C) Mutation in PLCD1 in families A and B.
(B) Family A; homozygous mutation c.1309C>T, p.Arg437X in an affected individual V-4 (top); heterozygous mutation in an unaffected carrier V-6 (bottom).
(C) Family B; homozygous mutation c.1792-10delTGTAGTGGCC in affected member V-2 and heterozygous in carrier member V-1 of family B.
(D) Heterozygous c.1720C>T (antisense strand), p.Ala574Thr in family C.
(E) Heterozygous c.625T>C, p.Cys209Arg in family D.
(F) Function of p.Arg437X mutant PLCD1 protein in vitro by detection of phospholipase C downstream metabolite IP1. The quantity of IP1 was measured by ELISA 48 hr after transfection of HEK293T cells with vector only (negative control), vector and wild-type PLCD1 construct (positive control), and vector and mutant PLCD1 construct. The test was repeated five times and difference was statistically significant (p < 0.01).
