Figure 2.
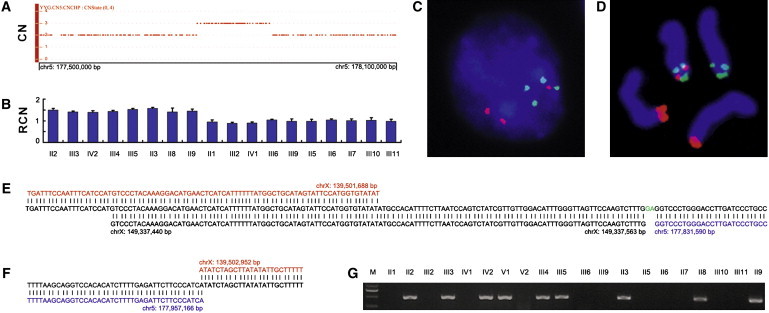
Identification of an Inherited Interchromosomal Insertion at Xq27.1 in the Chinese Family with a Distinct X-Linked Congenital Hypertrichosis Syndrome
(A) Copy-number state of a 600 kb genomic region on chromosome 5q35.3 showing the presence of a microduplication in the proband. CN, copy number.
(B) Validation of the microduplication and its segregation with the disease phenotype by qPCR. RCN, relative copy number. Error bars represent SD.
(C and D) Two-color FISH signals on a representative interphase nucleus (C) and typical metaphase chromosomes (D) demonstrating the insertion event. BAC probes are CTD-2507I18 (red), RP11-55E17 (green), and RP11-671F22 (green). See Figure 4A for the positions of BAC clones.
(E and F) Sequence analysis of the proximal (E) and distal (F) insertion junctions. Reference sequences on Xq27.1 and 5q35.3 are indicated in red and blue, respectively. The proximal junction contains a microinsertion from the X chromosome (black) and a 2 bp microinsertion (green) of unknown origin.
(G) PCR amplification of the distal insertion junction showing segregation of the insertion with the phenotype.
All genomic positions correspond to the February 2009 human reference sequence (GRCh37).
