Figure 4.
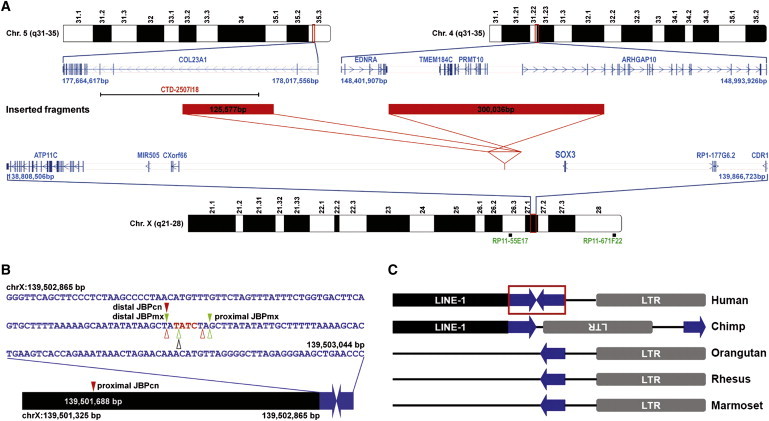
Interchromosomal Insertions Mediated by the Same Human-Specific Palindrome
(A) Schematic diagram depicting the two independent insertions found in the present study. Red solid bars represent the inserted fragments, and indicated sizes correspond to base pairs (bp). Red lines display the orientation of insertions. Positions of the BAC probes used in two-color FISH and of the RefSeq genes on the corresponding chromosomal regions are shown.
(B) Schematic diagram of the 180 bp human-specific palindrome with a summary of the breakpoints identified in the present study. Solid triangles indicate insertion breakpoints in the two study families (Chinese in red and Mexican in green). JBPcn, junction breakpoint in the Chinese family; JBPmx, junction breakpoint in the Mexican family. Open triangles represent the deletion breakpoints in normal individuals (Chinese in red, Mexican in green, and Yoruban in black). A black solid bar represents the LINE-1 element that contains the proximal JBPcn. The precise position of the JBPcn is given.
(C) Schematic diagram showing the small human-specific palindrome at Xq27.1 and its flanking sequences. The 180 bp palindromic sequence is boxed. A chimp has two halves of the palindrome but in direct orientation. All other three nonhuman primates only have one half of the palindrome.
All genomic positions correspond to the February 2009 human reference sequence (GRCh37).
