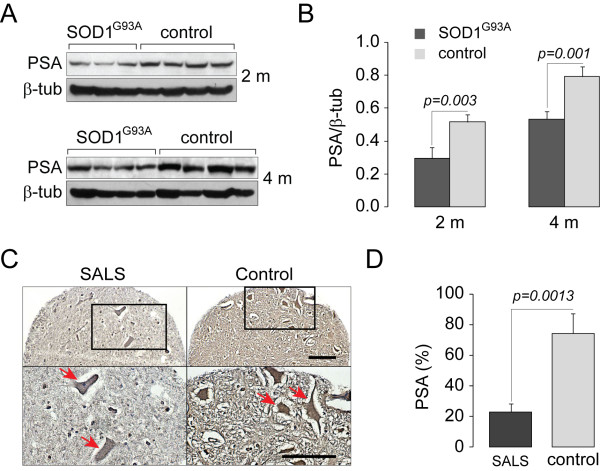
Figure 3.
PSA/NPEPPS is significantly decreased in both SOD1G93A transgenic mice and motor neurons of postmortem SALS patients. A, B. PSA/NPEPPS protein expression analyzed with Western blot is significantly decreased in the spinal cord of 2 months old (2 m) adult presymptomatic (n = 4) and 4 months old (4 m) symptomatic (n = 4) SOD1G93A transgenic mice compared to the corresponding littermate 2 (n = 4) and 4 (n = 4) months old wild-type mice. C, D. A high-throughput immunohistochemical analysis using SALS tissue microarray reveals a significant decrease of PSA/NPEPPS-positive anterior horn motor neurons in SALS patients (n = 19) compared to healthy controls (n = 6). C. Representative spinal cord anterior horn tissue cores from SALS and control subjects show that PSA/NPEPPS protein expression is reduced in SALS motor neurons. Scale bar 20 μm. D. Bar graphs summarizing the findings from SALS tissue microarray show significant decrease of PSA/NPEPPS in SALS motor neurons. On average, each SALS (n = 19) and control (n = 6) subject was represented by ten spinal cord anterior horn tissue cores [38]. Error bars represent standard deviations.