Figure 4.
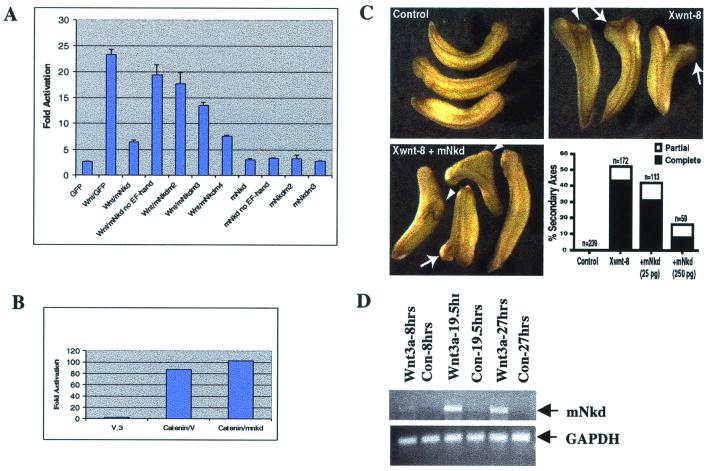
mNkd inhibits the canonical Wnt pathway and mNkd-mRNA level is up-regulated by Wnt. (A) HEK293 cells were transfected with expression constructs that included 0.02 μg of LEF-1, 0.2 μg of luciferase reporter (25), 0.02 μg of pRL-TK (Promega), 0.1 μg of pCGWnt-1, and 0.2 μg of GFP, mNkd, or mNkd-mutant derivatives. LEF-1 luciferase reporter activities were determined. (B) mNkd did not inhibit the β-catenin-activated Lef-1 reporter. HEK293 cells were transfected with expression constructs that included 0.02 μg of LEF-1, 0.2 μg of luciferase reporter (25), 0.02 μg of pRL-TK (Promega), 0.1 μg of β-catenin, and 0.2 μg of vector or mNkd. (C) mNkd inhibited Xwnt-8-induced secondary axes formation in Xenopus. Control Xenopus embryos are shown at Upper Left. Embryos were injected ventrally with 5–10 pg of Xwnt-8 RNA and developed with secondary axes (Upper Right). Secondary axes were scored as complete (arrows) or partial (arrowheads) based on development of anterior structures such as eyes and cement glands. Coexpression of mNkd with Xwnt-8 decreased the frequency of secondary axes formation as well as the percentage of secondary axes that contained anterior structures (Lower Left and Lower Right). This effect was dose-dependent. (D) BALB/c LI mouse liver epithelial cells were treated with either Wnt-3a or Neo-conditioned medium (34) for indicated hours. PCR was carried out by using primer pairs 5′-TGTGAACCATTCCCCCACATCAA-3′ and 5′-AAATGGGGTGTCAAGGAGGTGGAA-3′. The PCR products were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate control.