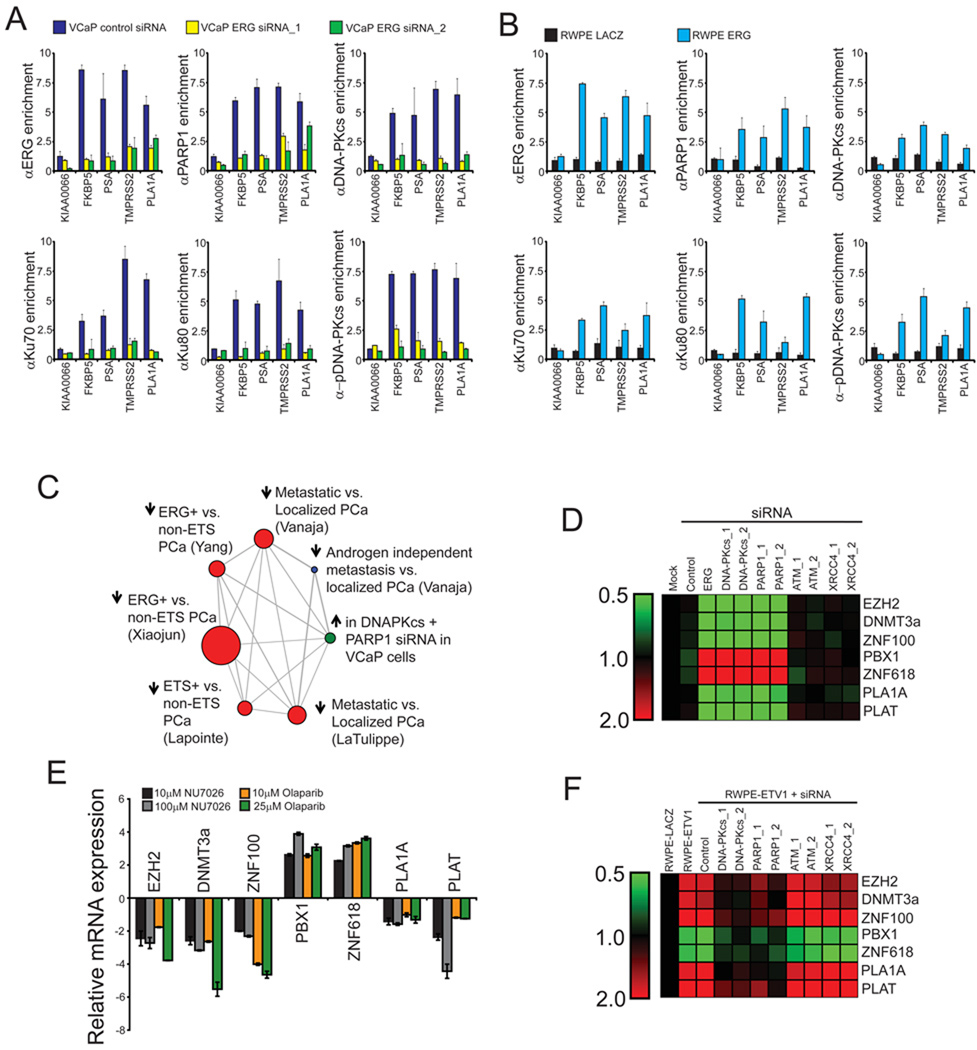
Figure 2. PARP1 and DNA-PKcs are required for ERG-regulated transcription.
(A) ChIP of PARP1 and the DNAPK complex shows an association with ERG-regulated targets including the PLA1A promoter as well as FKBP5 PSA and TMPRSS2 enhancers, but not the negative control gene KIAA0066. ChIPs were performed in VCaP cells treated with control or one of two independent ERG siRNAs for 48 hours prior to cross-linking.
(B) ChIP performed as in (A), but with stable RWPE-ERG or -LACZ cells.
(C) Data from gene expression arrays was analyzed by molecular concept mapping. The gene set analyzed is the set of genes that were greater than 2-fold differential in all three siRNA treatments relative to control. This gene set was used to determine the correlation of genes regulated by ERG, DNA-PKcs and PARP1 in VCaP cells with published microarray data. Node size is proportional to the number of genes in the set and edges represent statistically significant associations (p < 0.01). Arrow directionality represents gene sets either being induced or repressed.
(D) VCaP cells were treated with siRNA as indicated 48 hours prior to RNA isolation. qPCR was then run to confirm gene expression changes identified in the microarray experiment. Data is shown as a heat map with siRNA treatments along the x-axis and genes whose expression was analyzed by qPCR along the y-axis. Shades of green represent down-regulation of gene expression while shades of red represent up-regulation.
(E) VCaP cells were treated with either NU7026 or Olaparib for 48 hours as indicated and qPCR analysis of ERG-target genes identified from gene expression microarray experiment was performed.
(F) As in (D), except stable RWPE-ETV1 cells were used. All qPCR experiments were run three times in quadruplicate.
All bar graphs are shown with +/− SEM unless otherwise indicated. See also Figure S2 and Table S2.