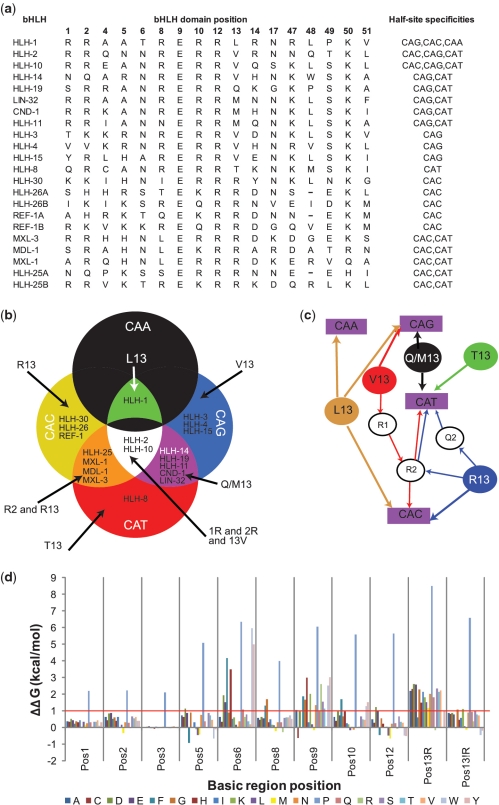
Figure 3.
bHLH domain amino acids correlate with E-box half-site recognition (a) Amino acid residues at each position in C. elegans bHLH proteins that are involved in DNA contacts. The final column shows the list of recognized half-sites for each bHLH (7). ‘A’ and ‘B’ (e.g. HLH-26A and HLH-26B) refer to the first and second bHLH domain of two within the same protein. (b) Diagram illustrating the distribution of bHLH proteins according to their half-site specification. (c) Schematic representation of the rules inferred from (a) and illustrated in (b). Filled circles represent residues at position 13; purple rectangles represent half-sites and open circles represent specific sequence determinants for linking residue 13 to a particular half-site. (d) Graphical representation of the average ΔΔGint per mutation for the seven bHLH structures analyzed. Mutations for which ΔΔGint is larger than 1.0 kcal/mol (indicated by the red line) may have considerably diminished, or even abolished, the binding capabilities of the mutant. Position 13 is split between the average ΔΔGint for the scaffold of bHLH proteins that normally do or do not have an arginine in that position.