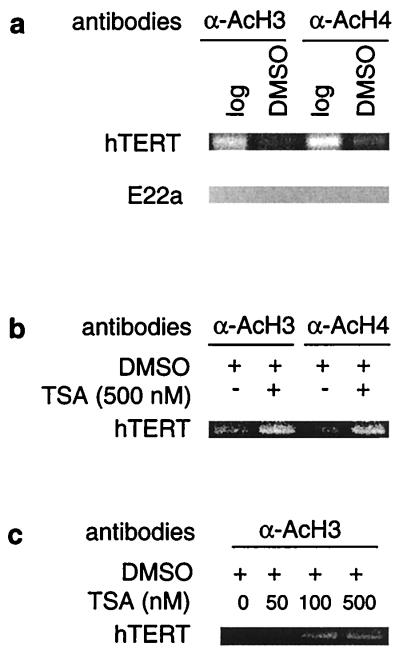
Figure 3.
Changes in histone acetylation at the hTERT promoter and TSA-mediated hyperacetylation of histones during HL60 differentiation. A ChIP assay was performed on logarithmically growing and DMSO-treated HL60 cells as described in Materials and Methods. (a) A decrease in acetylation of H3 and H4 histones at the hTERT promoter in differentiated HL60 cells. The absence of acetylated histones at the E22a fragment that contains an E-box but is not transcribed. Log, logarithmically growing cells; DMSO, DMSO-treated (differentiated) cells. (b) Abolishment of the differentiation-associated deacetylation of histones H3 and H4 at the hTERT promoter by TSA treatment in HL60 cells. Cells were induced to differentiate by DMSO overnight in the absence or presence of TSA as indicated. (c) TSA-mediated dose-dependent accumulation of histone H3 at the hTERT promoter in differentiating HL60 cells. Cells were treated with DMSO overnight in the absence or presence of various concentrations of TSA as indicated.