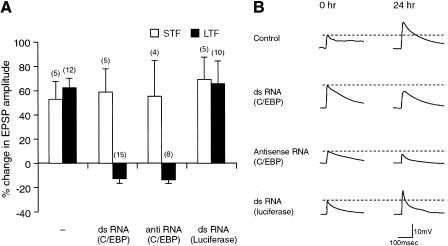
Figure 6.
Inhibition by double-strand RNA of ApC/EBP expression blocks long-term facilitation in the sensory-motor synapse. (A) Bar graph representing the effect of ApC/EBP double-strand RNA on short-term (STF, open bars) and long-term facilitation (LTF, solid bars). Injection of either ApC/EBP double-strand RNA or antisense RNA blocked long-term facilitation induced by five pulse of 5-HT, but injection of luciferase double-strand RNA did not. In contrast, injection of ApC/EBP double-strand RNA, ApC/EBP antisense RNA, or luciferase double-strand RNA did not affect short-term facilitation induced by one pulse of 5-HT. The height of each bar corresponds to the mean percentage change ± SEM in EPSP amplitude tested after 5-HT treatment. (−) No injection of double-strand RNA. A one-way analysis of variance and Duncan's multiple range test were used to determine the significance of the EPSP changes by long-term facilitation (F = 21.99, df = 3, P <0.001). (B) Examples of EPSP recorded in motor neuron LFS after stimulation of the sensory neurons before (0 h) and 24 h after five pulses of 5-HT (10 μM) treatment. Control, no injection of double-strand RNA.