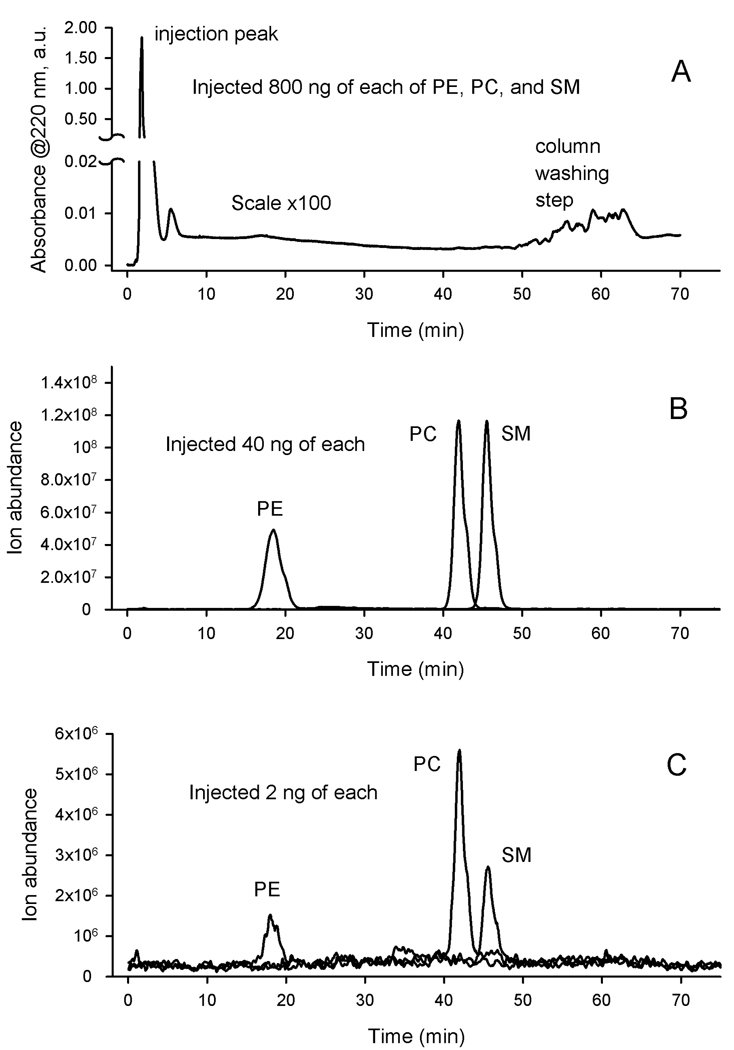
Figure 14.
Comparison of HPLC-UV and HPLC-MS approaches to phospholipid analysis.
Panel A. An NP HPLC-UV method adopted from [63] was used to analyze a mixture of PE, PC, and SM. An aliquot of the mixture (800 ng of each lipid) was injected and the elution profile of the lipids was monitored at 220 nm. Note that there was no HPLC peaks of the phospholipids observed after the initial injection peak. A conclusion can be made that because of its insensitivity, the HPLC-UV approach is not suitable for analyzing complex lipid mixtures with small amounts of phospholipids, such as human meibum.
Panel B. The same mixture of three lipids was analyzed by NP HPLC-ESI MS in positive ion mode. Note that only a 40 ng aliquot of each lipid was injected. Three lipids were clearly visible with a negligible background noise.
Panel C. The same mixture of three lipids was analyzed by NP HPLC-ESI MS in positive ion mode. Note that this time only a 2 ng aliquot of each lipid was injected. Three lipids were still detectable albeit with a clearly declining signal-to-noise ratios.