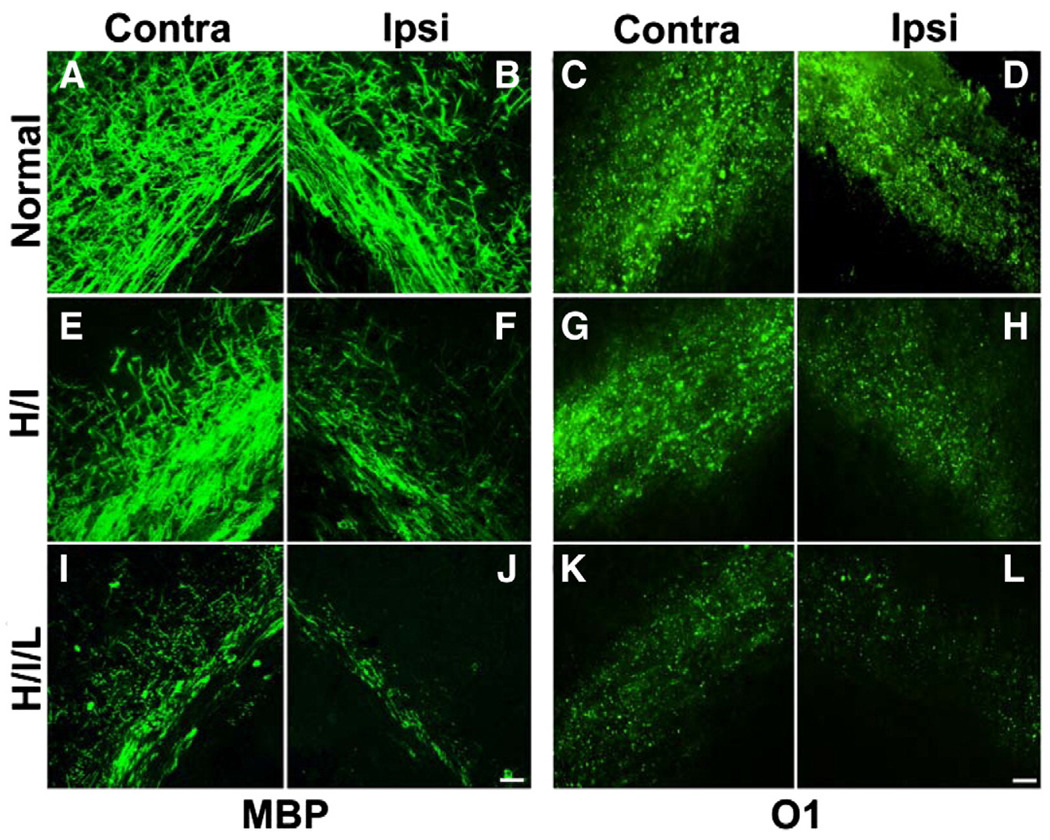
Fig. 2.
Oligodendrocyte loss and myelin depletion occur after H/I or H/I/L. White matter injury was induced by UCL and hypoxia exposure (H/I) or UCL combined with hypoxia exposure and LPS administration (H/I/L). (A–B) The corpus callosum of normal mice exhibited strong MBP immunoreactivity. After H/I, MBP expression decreased substantially in the ipsilateral side with a slight reduction in the contralateral side as well (E–F). After exposure to H/I/L, MBP-immunoreactivity diminished substantially in both the ipsilateral and contralateral white matter track (I–J). Similarly, normal mice showed substantial and equal O1 immunoreactivity in the corpus callosum of both hemispheres (C–D) while mice exposed to H/I exhibited a dramatic reduction in O1 staining in the ipsilateral corpus callosum (G) but no change in O1 staining in the contralateral white matter (G). Mice exposed to H/I/L displayed a dramatic reduction in O1 immunoreactivity in both white matter tracks (K–L). Scale bar, 10 µm. Contra = contralateral, Ipsi = ipsilateral.