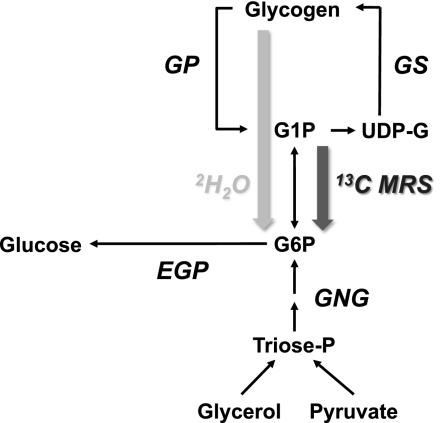
FIG. 1.
Metabolic model representing fluxes between G6P, glycogen, glucose, and the parameters of glycogenolytic flux derived by 2H2O and 13C MR methods. Component fluxes include GS flux, GP, GNG, and EGP. The in vivo 13C MRS assay measures the net loss of hexose from the pool of glycogen metabolites (i.e., net glycogenolysis), and GNG is calculated as EGP − net glycogenolysis. Net glycogenolysis represents the difference between GP and GS, hence the fraction of EGP derived from net glycogenolytic flux is equal to (GP − GS)/EGP. The 2H2O method measures the fractional contribution of GP to EGP flux. When GS is zero, net glycogenolysis and GP are equal. During glycogen cycling, where GS is active, GP is higher than net glycogenolysis.