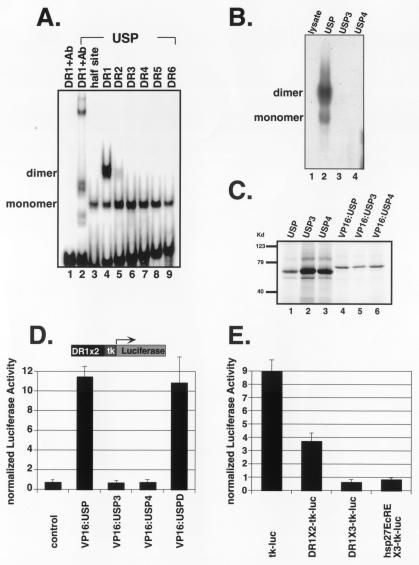
Figure 5.
The USP homodimer/DR1 complex is disrupted by USP3 and by USP4. (A) Gel mobility shift experiments in which 32P-labeled serial DR elements were incubated with bacterially expressed His-tagged USP. USP binds as a monomer on a half site, as well as on all DR elements (lanes 3–9); the USP homodimer specifically binds DR1 (lane 4). A USP specific antibody (AB11) was used in lanes 1 and 2. (B) Gel mobility shift in which a 32P-labeled DR1 element was incubated with mock translation mix (lane 1), in vitro translated USP (lane 2), USP3 (lane 3), or USP4 (lane 4). (C) In vitro translated 35S-labeled proteins corresponding to USP and its variants. (D) Transient transfection in CV-1 cells with a reporter, DR1 × 2-tk-luc, and pCMX-based plasmids expressing VP16:USP (lane 2), VP16:USP3 (lane 3), VP16:USP4 (lane 4), or VP16:USPD (lane 5). USPD represents the DNA-binding domain of USP (amino acids 50–205). In this and other experiments, luciferase activities were normalized by cotransfecting cells with CMX-lacZ, which expresses β-galactosidase. (E) Drosophila Schneider S2 cells were transfected with tk-luc (lane 1), DR1X2-tk-luc (lane 2), DR1X3-tk-luc (lane 3), and hsp27EcREX3-tk-luc (lane 4).